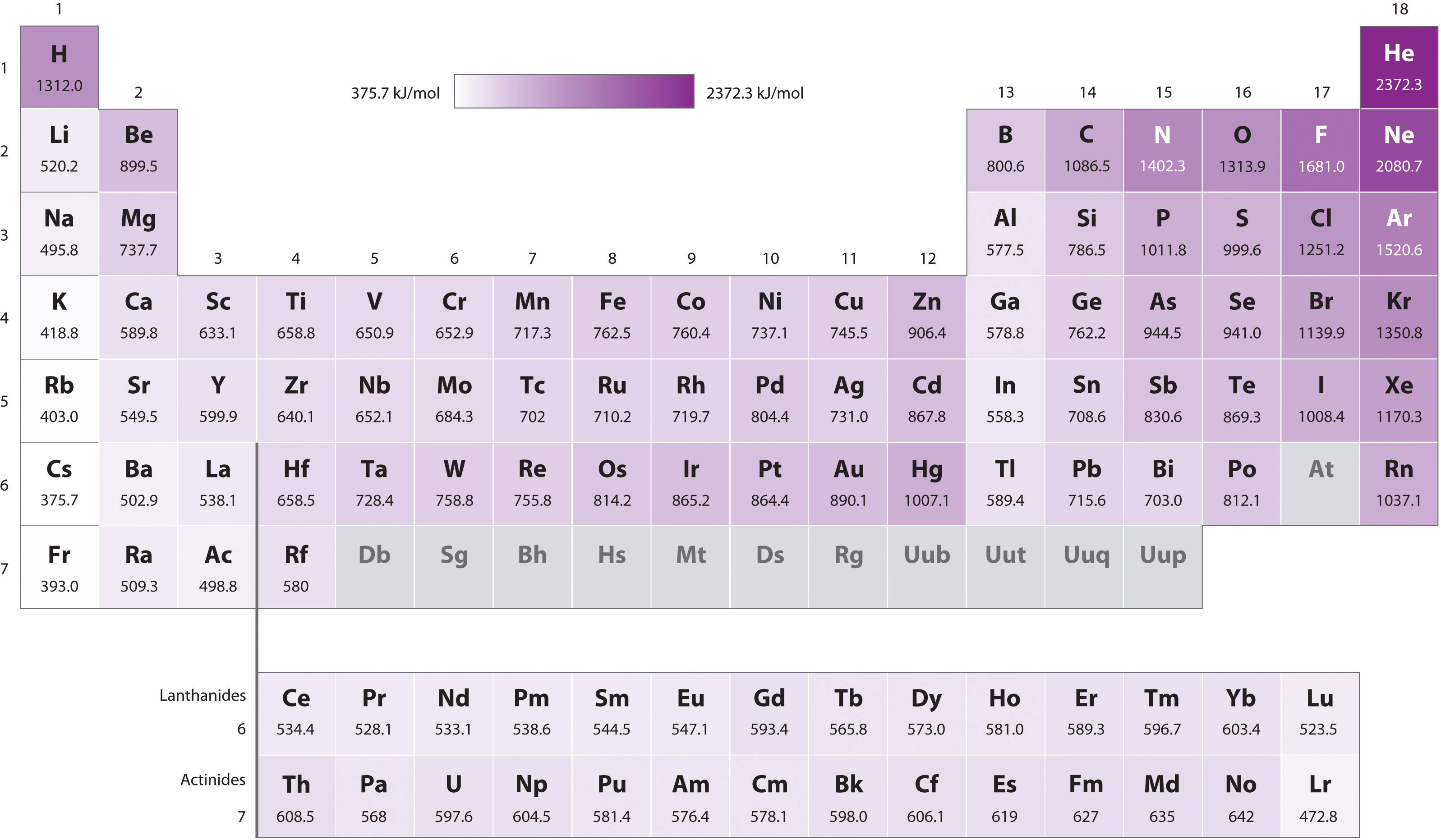
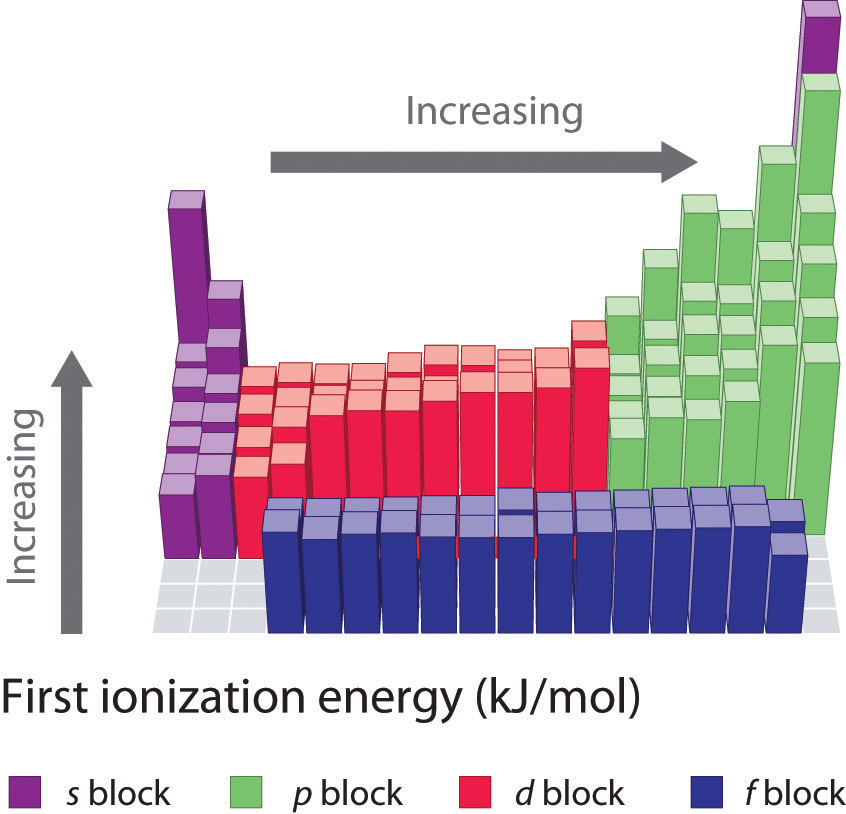
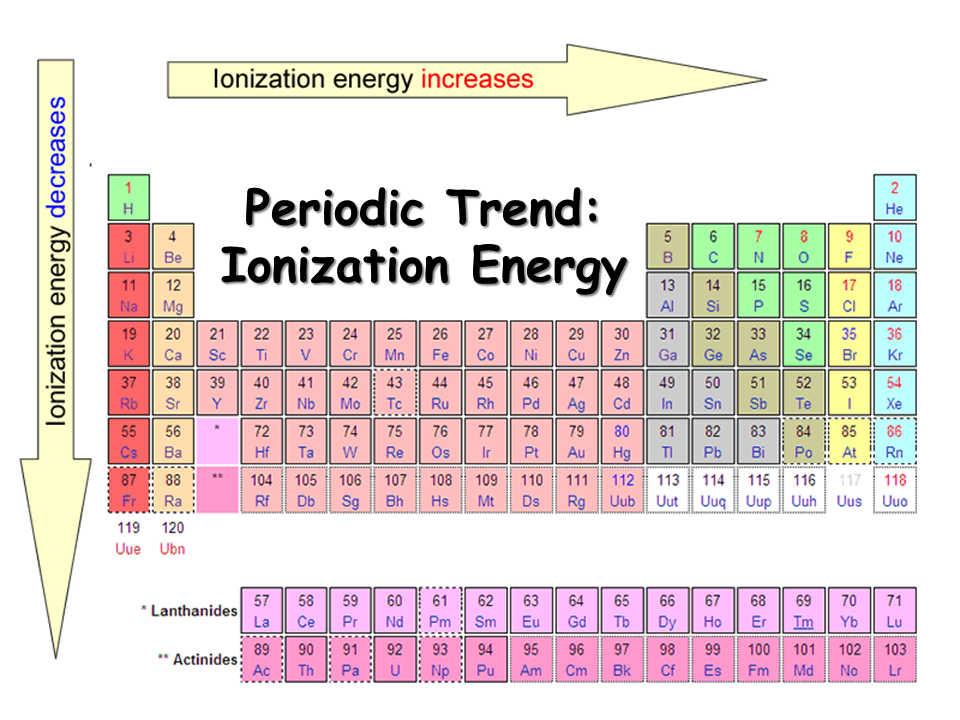
1St Ionization Energy Chart
1St Ionization Energy Chart - Web these tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kj⋅mol −1. Learn its chemical equation, values, trends across a period & down a group, & exception. Web an element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a neutral atom of the element. Web the symbol \(i_1\) stands for the first ionization energy (energy required to take away an electron from a neutral atom) and the symbol \(i_2\) stands for the second ionization energy (energy required to take away an electron from an atom with a +1 charge. Web the first ionization energies of the transition metals are somewhat similar to one another, as are those of the lanthanides. And we can see that abnormally large difference between the fifth and sixth ionization energies as expected. Each succeeding ionization energy is larger than the preceding energy. The first ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart below. Nist reference table on ground states and ionization energies for the neutral atoms. Image showing periodicity of the chemical elements for ionization energy: Up to date, curated data provided by mathematica 's elementdata function from wolfram research, inc. On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally decreases as you move down a group. 1011.8, 1907, 2914.1, 4963.6, 6273.9, 21267, 25431; Web explore how ionization energy changes with atomic number in the periodic table of elements via interactive plots. The first chemical element is cesium and the last one is helium. Web first ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart. Web these tables list values of molar ionization energies, measured in kj⋅mol −1. Image showing periodicity of the chemical elements for ionization energy: Web the first ionization energies of the transition metals are somewhat similar to one another, as are those of the lanthanides. The first molar ionization energy applies to the neutral atoms. Web ionization energies of the elements. The ionization energy is measured in joules (j) or electron volts (ev). Web complete and detailed technical data about the element $$$elementname$$$ in the periodic table. The first ionization energy is quantitatively expressed as. The tabular chart on the right is arranged by ionization energy. The first chemical element is cesium and the last one is helium. On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally decreases as you move down a group. Web ionization energies of the elements. Web for chemistry students and teachers: Web what is ionization energy. Because positive charge binds electrons more strongly, the second ionization energy of an element is always higher than the first. This is the energy per mole necessary to remove electrons from gaseous atoms or atomic ions. The tabular chart on the right is arranged by ionization energy. Web complete and detailed technical data about the element $$$elementname$$$ in the periodic. This is the energy per mole necessary to remove electrons from gaseous atoms or atomic ions. X (g) + energy x + (g) + e −. The first ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart below. Web an element's first ionization energy is the energy required to remove. Nist reference table on ground states and ionization energies for the neutral atoms. Web to confirm this here are the first seven ionization energies of phosphorus in kj/mol: To convert to kj/mol, multiply by 96.4869. Web the 1st ionization energy of the element m is a measure of the energy required to remove one electron from one mole of the. On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally increases as you move left to right across a period. And we can see that abnormally large difference between the fifth and sixth ionization energies as expected. The energy required to remove the outermost electron from an atom or a positive ion in its ground level. Web an element's first ionization energy. Web the 1st ionization energy of the element m is a measure of the energy required to remove one electron from one mole of the gaseous atoms m. The first chemical element is cesium and the last one is helium. In physics and chemistry, ionization energy ( ie) is the minimum energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron. Up to date, curated data provided by mathematica 's elementdata function from wolfram research, inc. Web for each atom, the column marked 1 is the first ionization energy to ionize the neutral atom, the column marked 2 is the second ionization energy to remove a second electron from the +1 ion, the column marked 3 is the third ionization energy. Web for each atom, the column marked 1 is the first ionization energy to ionize the neutral atom, the column marked 2 is the second ionization energy to remove a second electron from the +1 ion, the column marked 3 is the third ionization energy to remove a third electron from the +2 ion, and so on. This is the. Web an element's second ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a 1+ ion of the element. Because positive charge binds electrons more strongly, the second ionization energy of an element is always higher than the first. On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally increases as you move left to right. Web an element's second ionization energy is the energy required to remove the outermost, or least bound, electron from a 1+ ion of the element. The unity for ionization energy is ev. The energy required to remove the outermost electron from an atom or a positive ion in its ground level. Web complete and detailed technical data about the element $$$elementname$$$ in the periodic table. Nist reference table on ground states and ionization energies for the neutral atoms. Web the symbol \(i_1\) stands for the first ionization energy (energy required to take away an electron from a neutral atom) and the symbol \(i_2\) stands for the second ionization energy (energy required to take away an electron from an atom with a +1 charge. To convert to kj/mol, multiply by 96.4869. Web what is ionization energy. Web ionization energies of the elements. In physics and chemistry, ionization energy ( ie) is the minimum energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron of an isolated gaseous atom, positive ion, or molecule. Web first ionization energy, second ionization energy as well as third ionization energy of the elements are given in this chart. On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally increases as you move left to right across a period. Below are the chemical equations describing the first and second ionization energies: Web the first ionization energies of the transition metals are somewhat similar to one another, as are those of the lanthanides. Web predicted values are used for elements beyond 104. X (g) + energy x + (g) + e −.7.4 Ionization Energy Chemistry LibreTexts
The Parts of the Periodic Table
Periodic Variations in Element Properties Chemistry
7.4 Ionization Energy Chemistry LibreTexts
Ionization Enthalpy NEET Lab
Periodic Table Ionization Energy Chart
Ionization energy Definition & Facts Britannica
First Ionisation Energies (ALevel) ChemistryStudent
Periodic Properties of the Elements Chemwiki
1st Ionization Energy Chart
Also, Learn First & Second Ionization Energies.
Web First Ionization Energy (Kj/Mol)
Up To Date, Curated Data Provided By Mathematica 'S Elementdata Function From Wolfram Research, Inc.
Image Showing Periodicity Of The Chemical Elements For Ionization Energy:
Related Post: