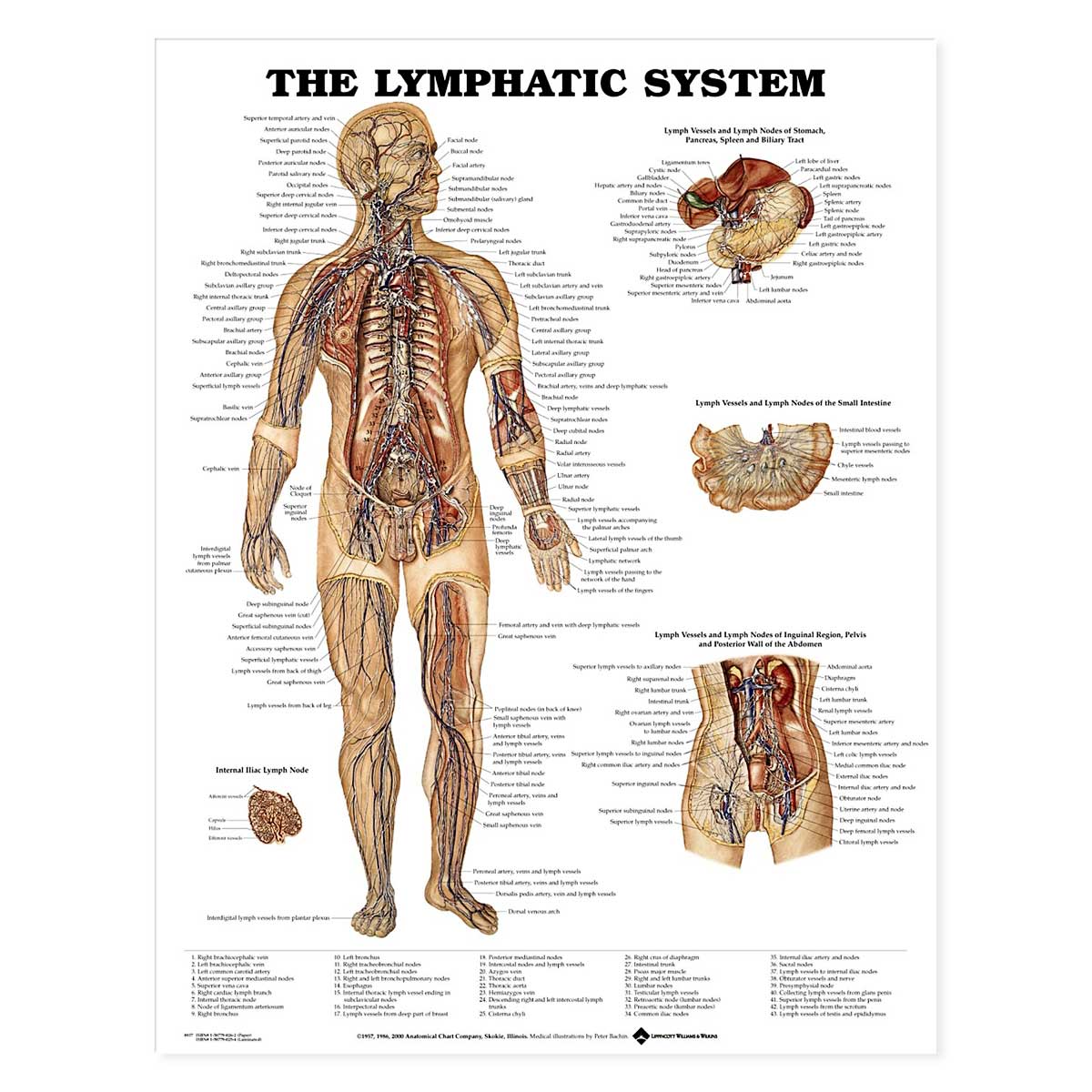
Chart Of Lymphatic System
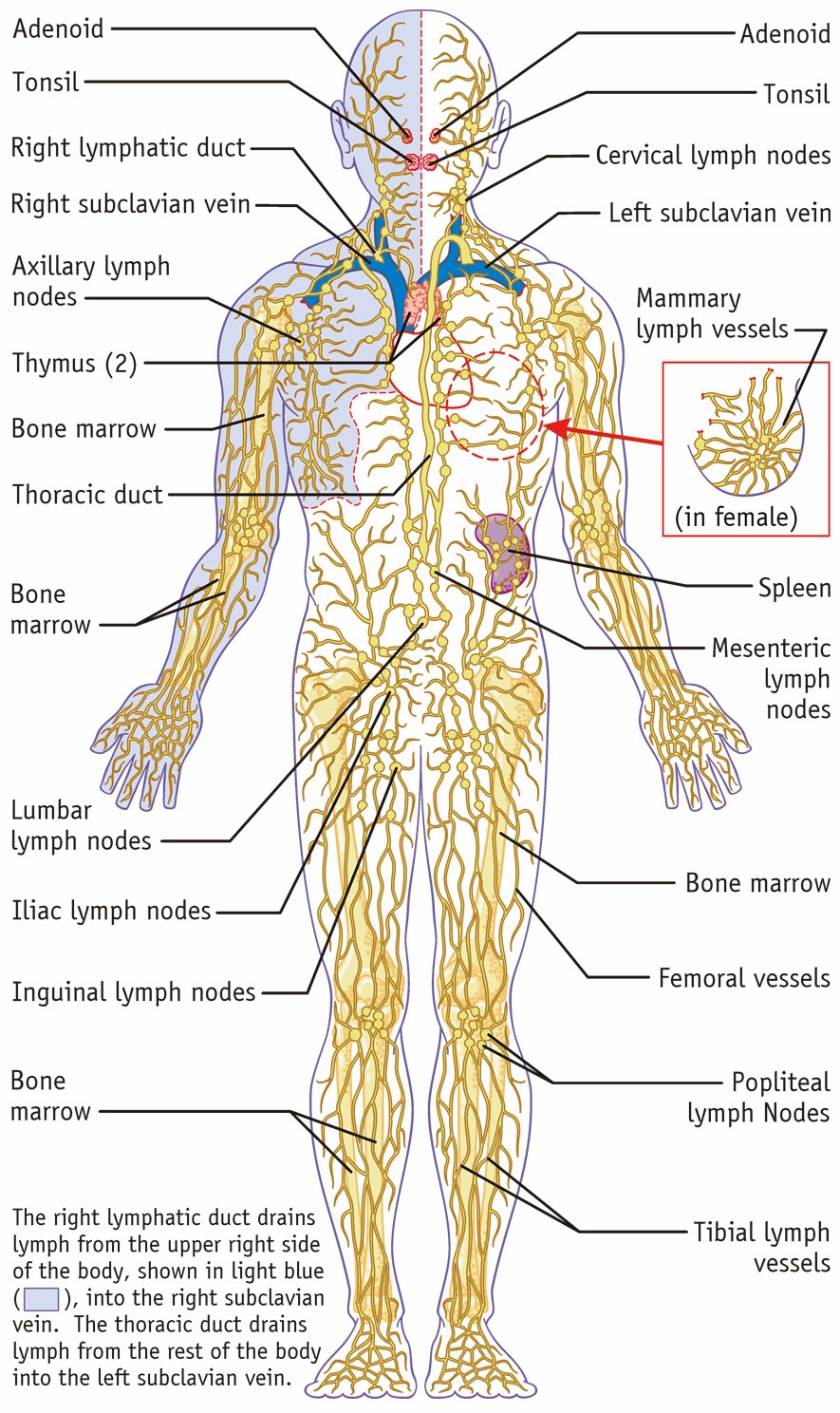
Chart Of Lymphatic System - Web the system moves lymph, a clear fluid containing white blood cells, through your bloodstream. Web circulation of lymph with flow chart. Web the lymphatic system partly functions to convey lymphatic fluid, or lymph, through a network of lymphatic channels, filter lymphatic fluid through lymph nodes and return lymphatic fluid to the bloodstream, where it is eventually eliminated. As well as the circulatory system and comprises the. (1) a meandering network of lymphatic vessels and (2) various lymphoid tissues and organs scattered throughout the body. Web the lymphatic system is a network of tissues and organs that help rid the body of toxins, waste, and other unwanted materials. Learn about lymph itself, bone marrow, and the different types of immunity. Web your lymphatic system is part of your immune system. Web learn all about the vessels, nodes, nodules, and ducts of the lymphatic system. This article gives a diagrammatic representation of the lymphatic system and its anatomy. The lymphatic system involves many organs, including the tonsils, adenoids, spleen, and thymus. They eventually drain into deep vessels. The chart shows the overall system of drainage in the body, the structure of lymph nodes and lymph vessels, and the formation of lymphocytes. By anatomical chart (author) 4.8 14 ratings. Your lymphatic system helps eliminate your body’s waste. Illustrates internal iliac lymph node, and lymph vessels & lymph nodes of the stomach, pancreas, spleen and biliary tract. It allows the circulation of a fluid called lymph through the body in a. It produces and releases lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) and other immune cells. Shows system throughout the body. Web lymph is composed of white blood cells, triglycerides, bacteria, cell debris, water, and protein. Web the system moves lymph, a clear fluid containing white blood cells, through your bloodstream. It has a composition comparable to blood plasma. Web the lymphatic vessels transport lymph fluid around the body. They eventually drain into deep vessels. By anatomical chart (author) 4.8 14 ratings. Web the lymphatic system is a network of vessels and organs that regulates the amount of fluid in the human body and defends it against infections. Web the lymphatic system • network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body’s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens • lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc •. Illustrates internal iliac lymph node, and lymph vessels & lymph nodes of the stomach, pancreas, spleen and biliary tract. They eventually drain into deep vessels. Web the lymphatic system is commonly divided into the primary lymphoid organs, which are the sites of b and t cell maturation, and the secondary lymphoid organs, in which further differentiation of lymphocytes occurs. Understanding. The lymphatic system involves many organs, including the tonsils, adenoids, spleen, and thymus. (1) a meandering network of lymphatic vessels and (2) various lymphoid tissues and organs scattered throughout the body. Web your lymphatic system is part of your immune system. In this article, we go into more detail about what lymphatic circulation is, how it works, why it is. Web the lymphatic system partly functions to convey lymphatic fluid, or lymph, through a network of lymphatic channels, filter lymphatic fluid through lymph nodes and return lymphatic fluid to the bloodstream, where it is eventually eliminated. Illustrates internal iliac lymph node, and lymph vessels & lymph nodes of the stomach, pancreas, spleen and biliary tract. ), the spleen, and the.. Web the lymphatic system anatomical chart illustrates internal iliac lymph node, as well as the lymph nodes and vessels of the stomach, pancreas, spleen, binary tract, small intestive, inguinal region, pelvis, and the posterior wall of the abdomen. It has a composition comparable to blood plasma. Lymph nodes filter out bacteria and cancer cells and create white blood cells to. Web the lymphatic system is commonly divided into the primary lymphoid organs, which are the sites of b and t cell maturation, and the secondary lymphoid organs, in which further differentiation of lymphocytes occurs. Web the lymphatic system • network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body’s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens • lymphatic. As well as the circulatory system and comprises the. It allows the circulation of a fluid called lymph through the body in a. Web the lymphatic system anatomical chart 3rd edition. Web the human lymphatic system: Primary lymphoid organs include the thymus, bone marrow, and fetal liver and, in birds, a structure called the bursa of fabricius. Learn about lymph itself, bone marrow, and the different types of immunity. Web circulation of lymph with flow chart. Web the lymphatic system partly functions to convey lymphatic fluid, or lymph, through a network of lymphatic channels, filter lymphatic fluid through lymph nodes and return lymphatic fluid to the bloodstream, where it is eventually eliminated. They range from tiny lymph. They range from tiny lymph capillaries to larger lymphatic ducts. Web the lymphatic vessels transport lymph fluid around the body. Web the lymphatic system anatomical chart illustrates internal iliac lymph node, as well as the lymph nodes and vessels of the stomach, pancreas, spleen, binary tract, small intestive, inguinal region, pelvis, and the posterior wall of the abdomen. Web the. Web lymph is composed of white blood cells, triglycerides, bacteria, cell debris, water, and protein. Web in the process, your lymphatic circulation system filters the fluid and works to remove toxins and potentially harmful waste. These cells look for and destroy invaders — such as bacteria, viruses, parasites and. It allows the circulation of a fluid called lymph through the body in a. Web learn all about the vessels, nodes, nodules, and ducts of the lymphatic system. This article gives a diagrammatic representation of the lymphatic system and its anatomy. They eventually drain into deep vessels. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, lymphatic tissue and lymph. Learn about lymph itself, bone marrow, and the different types of immunity. Web the lymphatic system anatomical chart 3rd edition. Web the lymphatic system • network of tissues, organs and vessels that help to maintain the body’s fluid balance & protect it from pathogens • lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, etc • without it neither the circulatory system nor the immune system would function • can be thought of as an accessory to the circulatory Web the lymphatic system chart lays out the structure of the system that helps with the body?s defenses against infection and disease. The lymph typically moves from lymphatic vessels to lymphatic trunks, collecting ducts, and ultimately into the subclavian veins. Your lymphatic system helps eliminate your body’s waste. Understanding the role of lymph nodes. The body is an elaborate network of systems and also organs, each with its very own important functions.Lymphatic system Structure, Function, & Facts Britannica
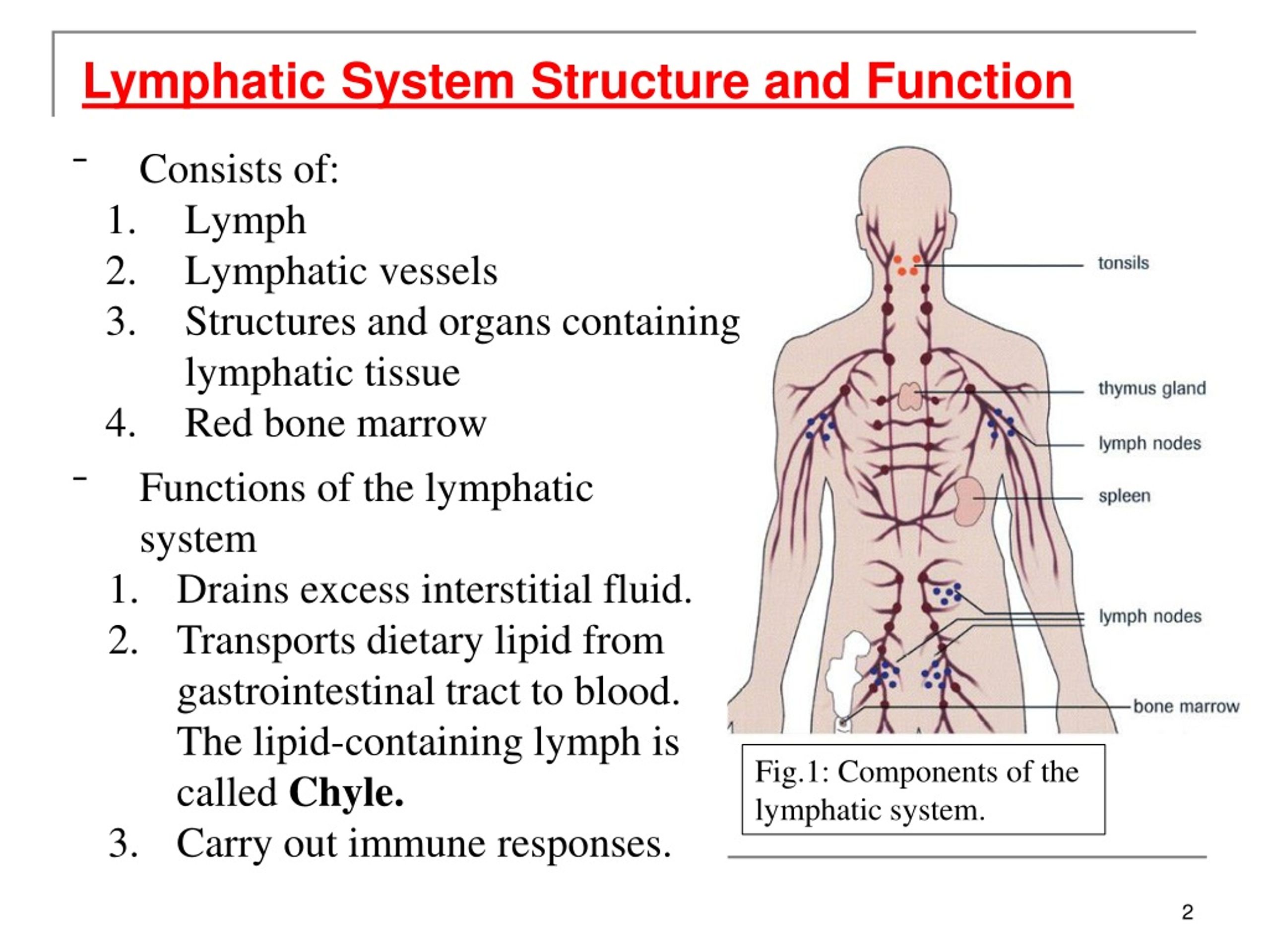
PPT The Lymphatic System PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
The Lymphatic System 2400 Anatomical Parts & Charts
Lymphatic system anatomy and physiology Artofit
Lymphatic System Flow Chart
What Is the Lymphatic System? [Infographic] DanaFarber Cancer Institute
Lymphatic System components, functions, applied
The Lymphatic System Anatomical Chart 20'' x 26''
Lymphatic System
Lymphatic system Wikipedia
The Lymphatic System Is Part Of The.
Primary Lymphoid Organs Include The Thymus, Bone Marrow, And Fetal Liver And, In Birds, A Structure Called The Bursa Of Fabricius.
The Pathway Of Lymph Is An Open Channel Where The Lymphatic Fluid Circulates.
3D Models Help You Explore The Anatomy And Physiology.
Related Post:



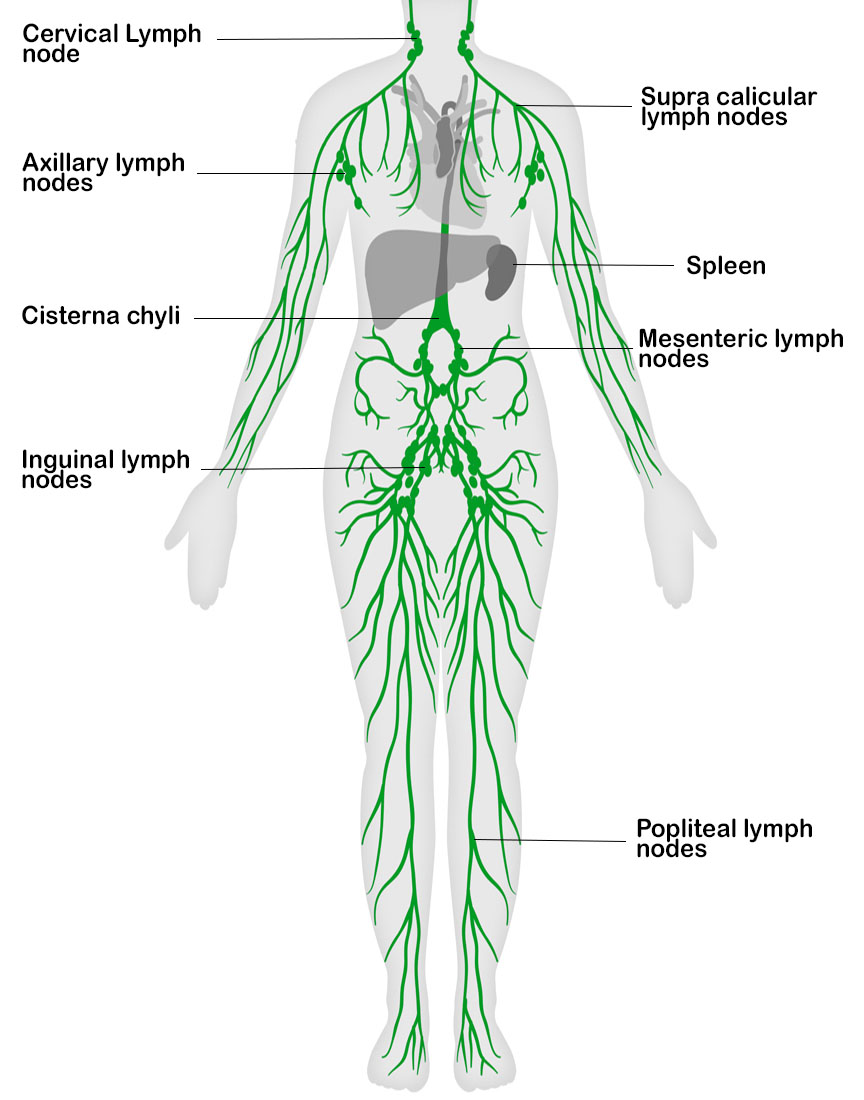
![What Is the Lymphatic System? [Infographic] DanaFarber Cancer Institute](https://blog.dana-farber.org/insight/wp-content/uploads/2016/09/7367-Lymphatic-System-Infographic-768x1217.png)