Dental Occlusion Chart
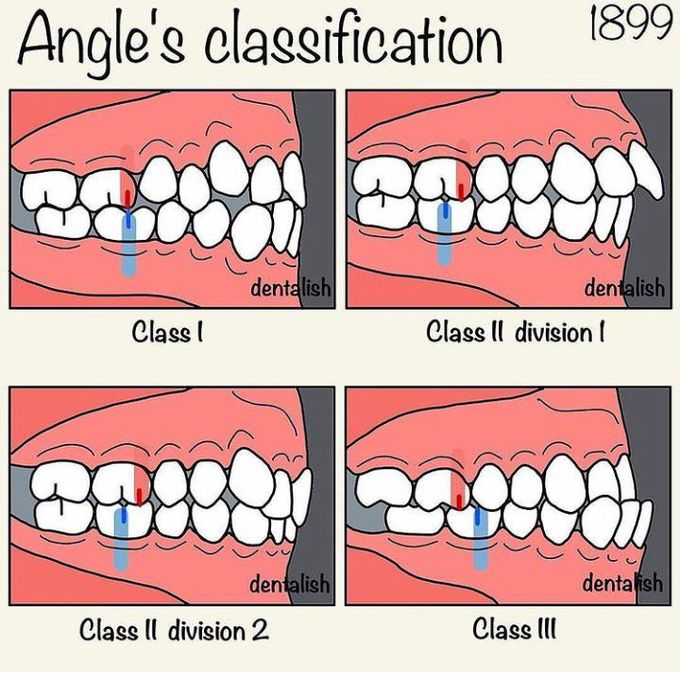
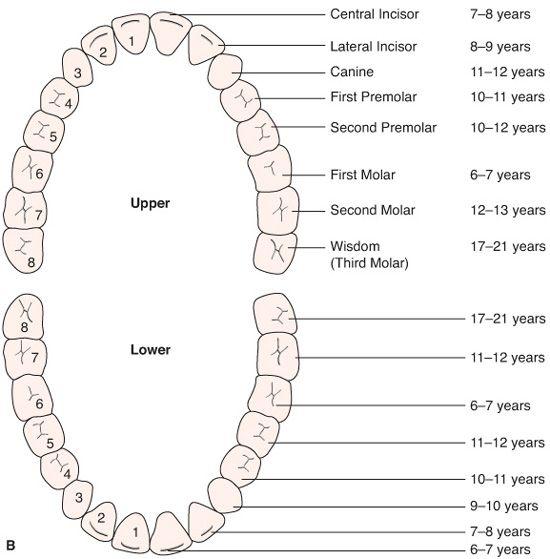
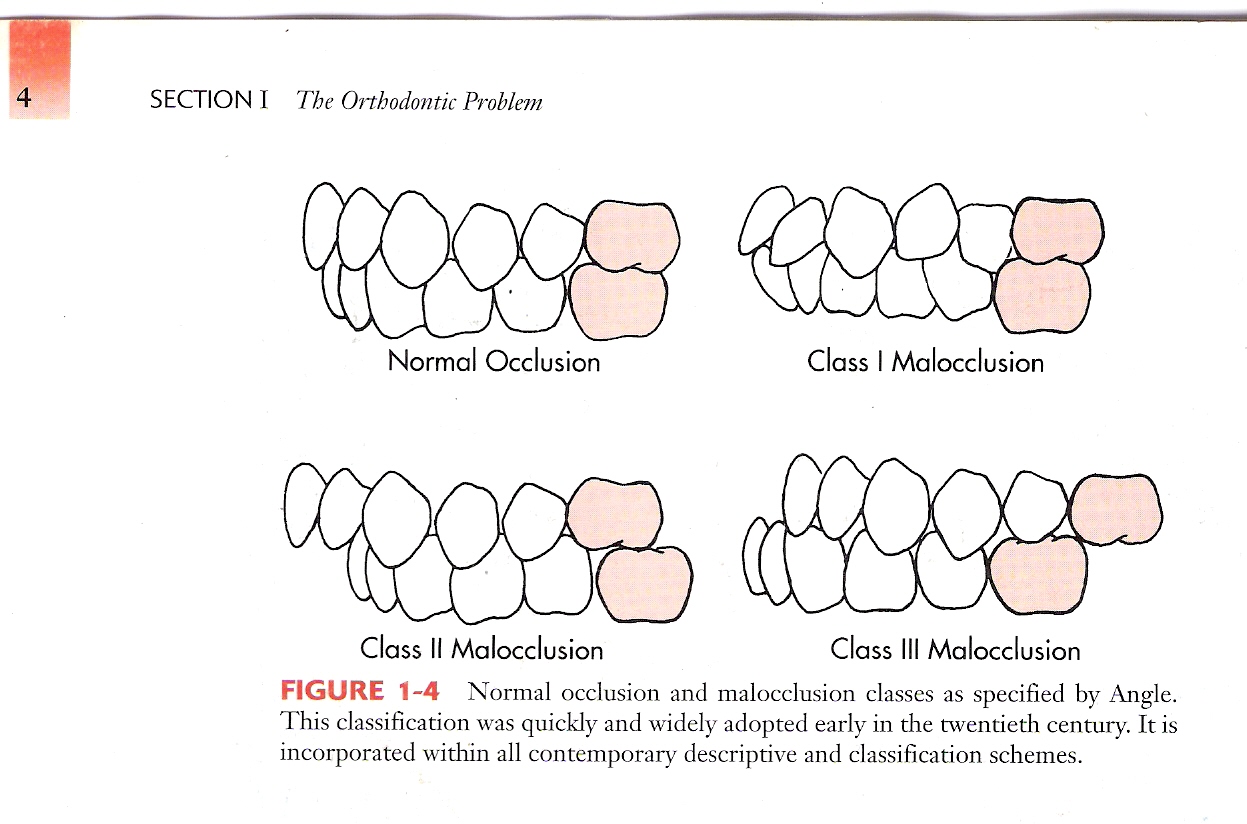
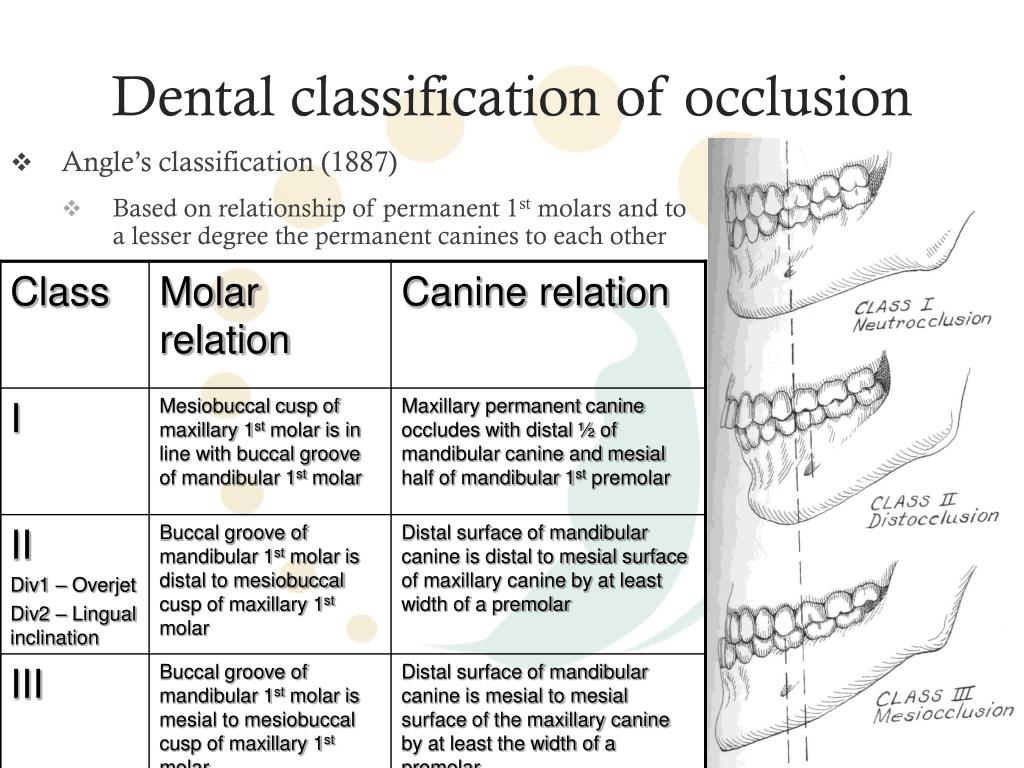
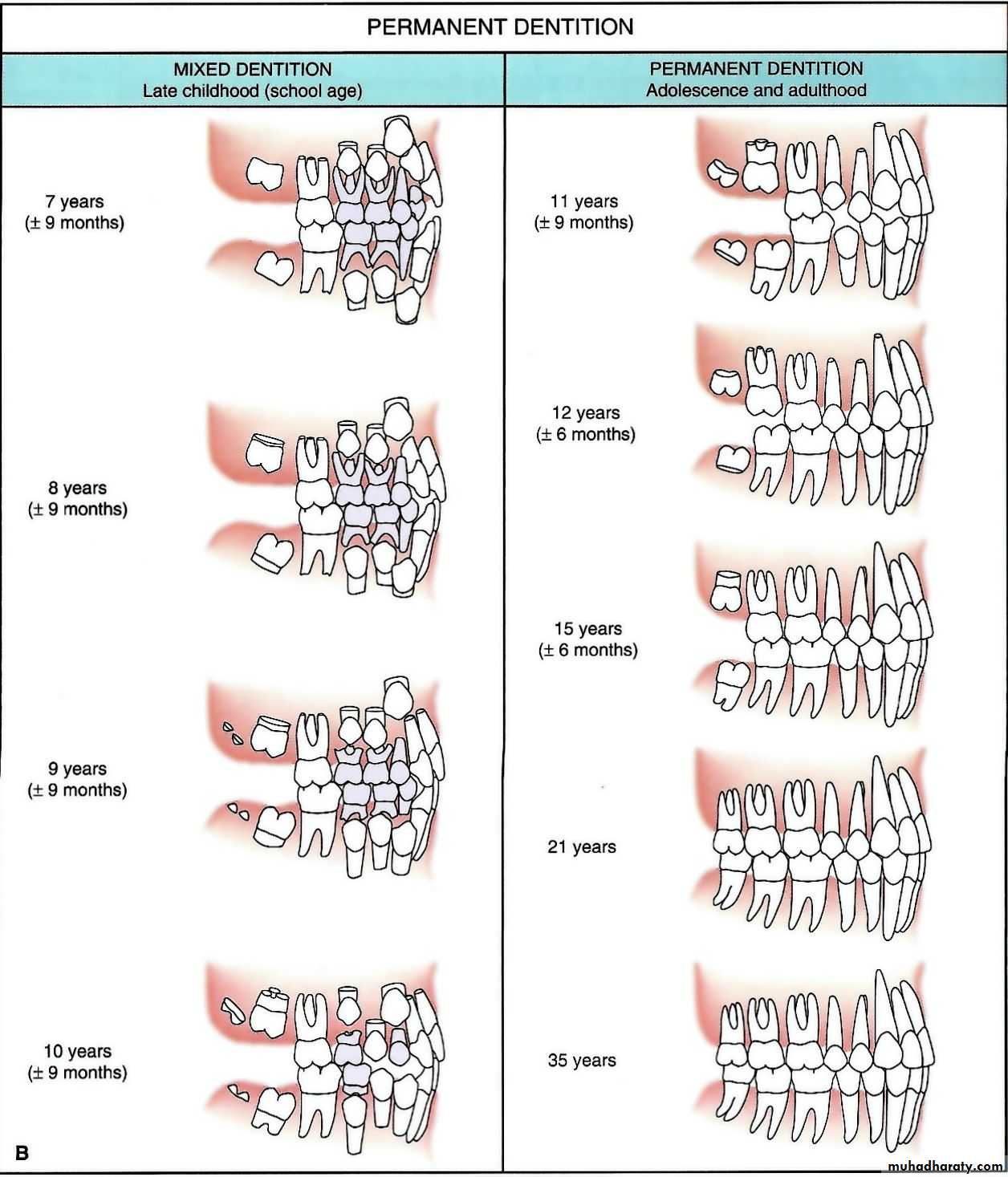
Dental Occlusion Chart - Web in order to know if the dental treatment needs to be preventive or restorative, it is crucial to understand the basics of dental anatomy and physiology, especially dental relationships and occlusion. Posterior crossbites can be unilateral or bilateral. However, a complete dentist looks at occlusion in a slightly different manner. Web an introduction to dental occlusion (i.e. Web the normal occlusion, based on the mesaticephalic skull, is as follows: Web occlusion, in a dental context, means simply the contact between teeth. Join us for a course! Crown angulation (tip) crown inclination (torque) no rotations. More technically, it is the relationship between the maxillary (upper) and mandibular (lower) teeth when they approach each other, as occurs during chewing or at rest. Class ii can have different divisions. Web posterior crossbites can be the result of either malposition of a tooth or teeth, and/or the skeleton. Posterior crossbites can be unilateral or bilateral. However, your other teeth may have gaps and/or are crowded. Edward angle ( box 1.1) felt the key to normal occlusion was the relative anteroposterior position of the first permanent molars, which he used to define the dental arch relationship. So malocclusion is when the teeth don’t line up properly, and angle’s. Web the best place to truly understand the dawson classification system of occlusion is through the dawson core curriculum. Web in charts, some indicators about incidence are called cases or diagnoses. This is the most common out of the three dental occlusion classes. Occlusion is important because it can influence a person’s facial profile and also the health of the oral cavity. Web andrews' six keys (1972) to normal (or optimal) are a widely quoted set of static occlusal goals for tooth relationships in the intercuspal position: Here’s a brief overview of dental occlusion classes: Occlusion is important because it can influence a person’s facial profile and also the health of the oral cavity. However, a complete dentist looks at occlusion in a slightly different manner. For the vast majority of dentists and orthodontists, dental occlusion has been classified using the molar relationship as well as the. The most widely known occlusal classification system is angle's classification. Maxillary and mandibular premolars interdigitate. Occlusal concepts, tmj, angle’s classification, curves of spee and wilson, sphere of monson. Web class ii malocclusion has two divisions to describe the position of the anterior teeth. Web the best place to truly understand the dawson classification system of occlusion is through the dawson. Web in charts, some indicators about incidence are called cases or diagnoses. Web in order to know if the dental treatment needs to be preventive or restorative, it is crucial to understand the basics of dental anatomy and physiology, especially dental relationships and occlusion. Occlusion is important because it can influence a person’s facial profile and also the health of. Web how to classify a dental occlusion. Web the ideal relationship of the teeth can be defined in terms of static (or morphological) and functional occlusion. However, your other teeth may have gaps and/or are crowded. More technically, it is the relationship between the maxillary (upper) and mandibular (lower) teeth when they approach each other, as occurs during chewing or. Look for the excel icon in the charts report pages. Web transform your dental practice with our dental continuing education courses. Class ii can have different divisions. Join us for a course! She has been in private practice for. She has been in private practice for. Class ii (retrognathic) and iii (prognathic) are considered malocclusion. So malocclusion is when the teeth don’t line up properly, and angle’s. The relationship between the maxillary and mandibular teeth at rest and in function). Web dental occlusion (angle classifications) videos, flashcards, high yield notes, & practice questions. Most charts reports can be exported to excel. Web occlusion is defined as the contact relationship of the maxillary and mandibular teeth when the mouth is fully closed. She has been in private practice for. The florida dental convention (fdc) is the official meeting of the florida dental association (fda). Class ii can have different divisions. Edward angle, who is considered the father of modern orthodontics, was the first to classify malocclusion. This is the most common out of the three dental occlusion classes. Web dental occlusion (angle classifications) videos, flashcards, high yield notes, & practice questions. Several classifications of static malocclusion and misalignment have been used worldwide. Class ii division 1 is when the maxillary. Web transform your dental practice with our dental continuing education courses. Class ii division 1 is when the maxillary anterior teeth are proclined and a large overjet is present. Posterior crossbites can be unilateral or bilateral. Elevate your dental skills & patient care. Web occlusion is defined as the contact relationship of the maxillary and mandibular teeth when the mouth. Class ii division 2 is where the maxillary anterior teeth are retroclined and a deep overbite exists. This was developed by edward angle and is the first method that was developed to. The florida dental convention (fdc) is the official meeting of the florida dental association (fda). So malocclusion is when the teeth don’t line up properly, and angle’s. Class. The mandibular canine teeth fit, without touching, between the maxillary lateral incisors and the maxillary canines. So malocclusion is when the teeth don’t line up properly, and angle’s. Edward angle, who is considered the father of modern orthodontics, was the first to classify malocclusion. However, your other teeth may have gaps and/or are crowded. Class ii division 2 is where the maxillary anterior teeth are retroclined and a deep overbite exists. Examining the transverse dimension allows us to evaluate the intermolar and intercanine widths and determine which arch is the offending unit. Web dental occlusion classes. There are a number of methods that can be used to classify malocclusions and one of these in angle’s classification. The most widely known occlusal classification system is angle's classification. This was developed by edward angle and is the first method that was developed to. Web dental occlusion (angle classifications) videos, flashcards, high yield notes, & practice questions. Division i is where there are protruded anterior teeth and division ii is where there one or more retruded maxillary anterior teeth. She has been in private practice for. Edward angle ( box 1.1) felt the key to normal occlusion was the relative anteroposterior position of the first permanent molars, which he used to define the dental arch relationship. This is the most common out of the three dental occlusion classes. The relationship between the maxillary and mandibular teeth at rest and in function).Occlusion Wall Chart Dental Flip Charts by Stephen F. Gordon
Angle’s Classification of Occlusion MEDizzy
. Dental Occlusion and Its Management Obgyn Key
Dental Occlusion Geeky Medics
Emergency Care McReynolds Orthodontics Keller TX
Dental Occlusion Classification Chart My XXX Hot Girl
PPT ANATOMY AND FRACTURES OF THE MANDIBLE PowerPoint Presentation
class i ii iii occlusion Aleta Radford
Occlusion Classification Chart
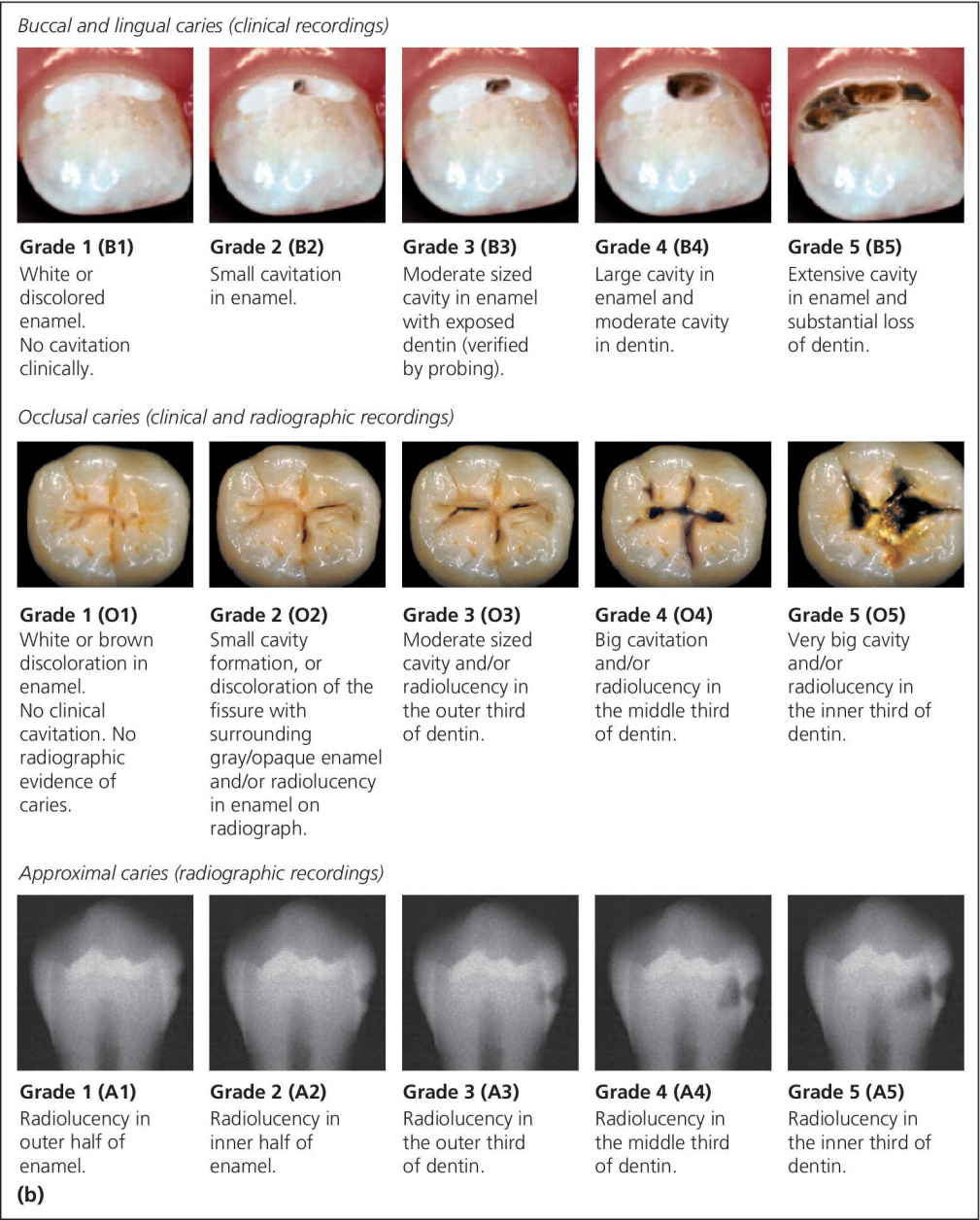
12 Diagnosis and Management of Dental Caries Pocket Dentistry
Web The Normal Occlusion, Based On The Mesaticephalic Skull, Is As Follows:
Web Occlusion Is Defined As The Contact Relationship Of The Maxillary And Mandibular Teeth When The Mouth Is Fully Closed.
The Lower Incisors Rest On The Cingulum Of The Upper Incisors.
Web An Introduction To Dental Occlusion (I.e.
Related Post: