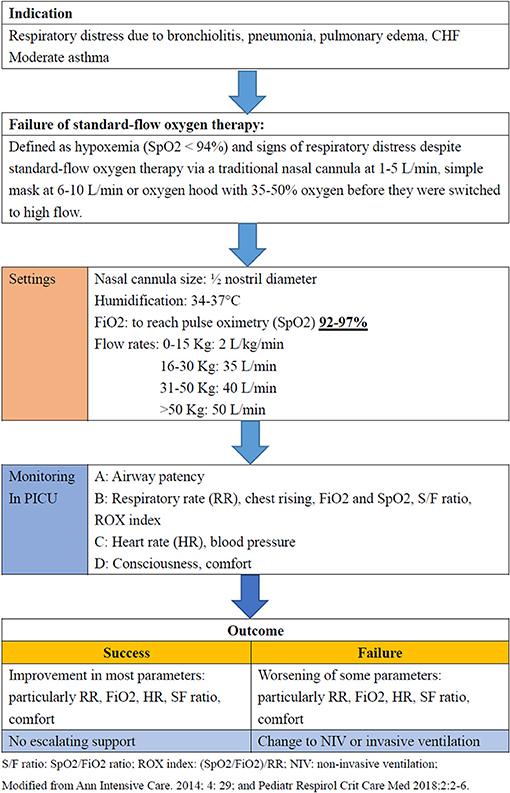
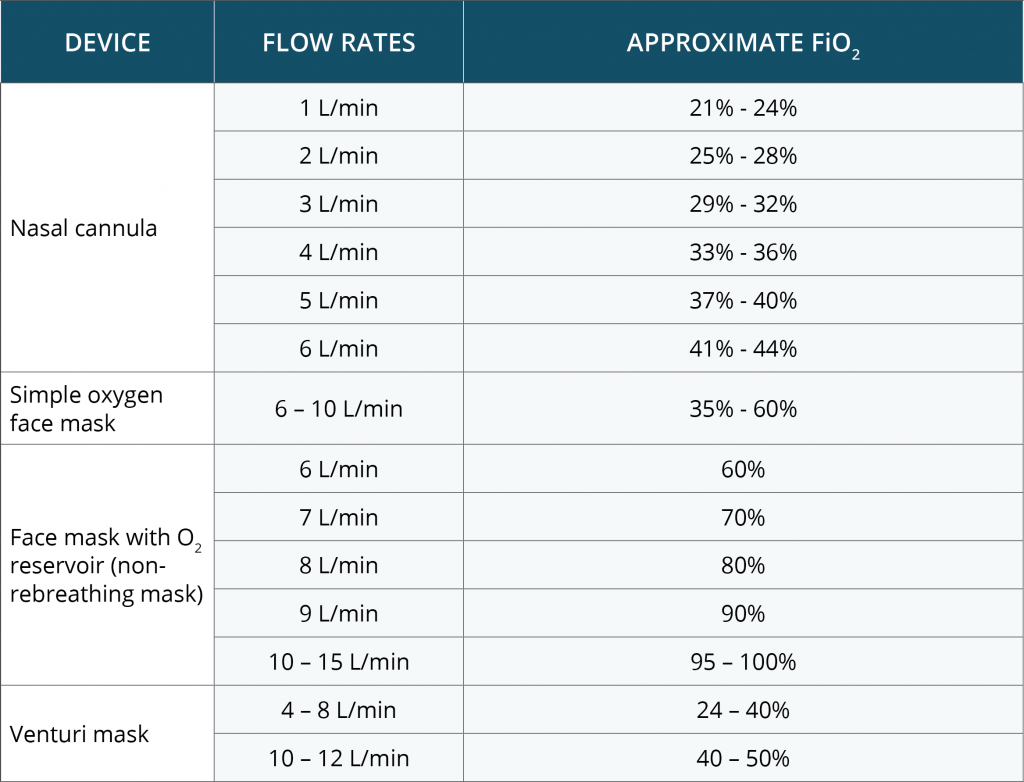
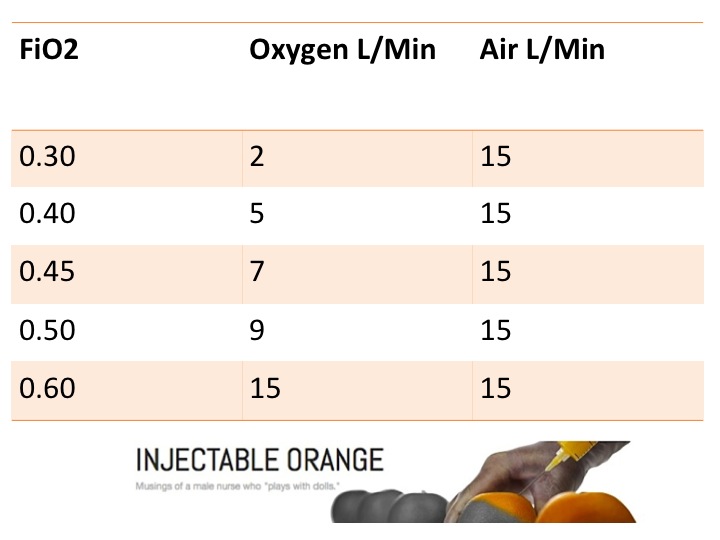
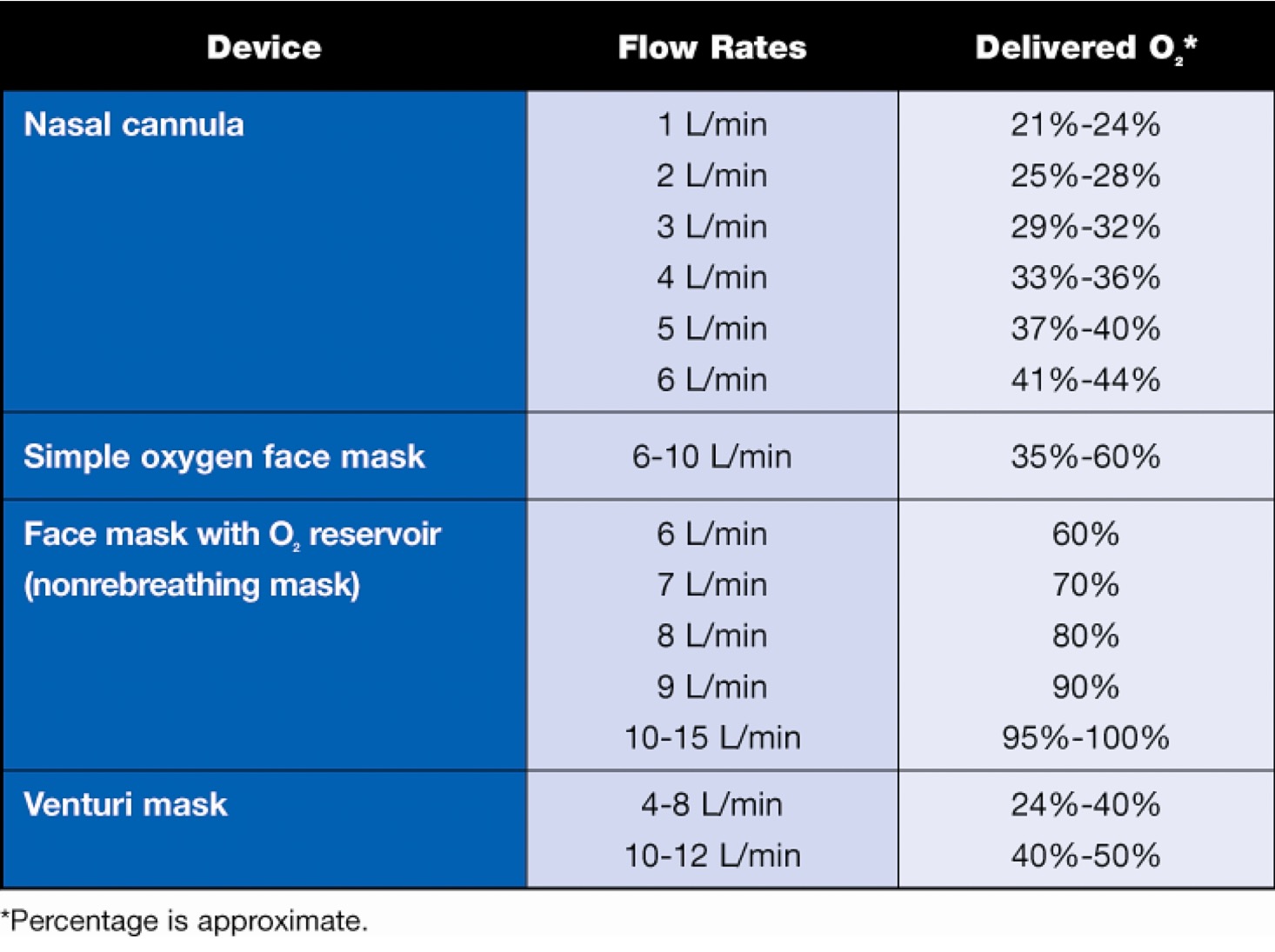
High Flow Nasal Cannula Fio2 Chart
High Flow Nasal Cannula Fio2 Chart - Heated humidified gas flow preserves nasal mucosa and is more comfortable allowing high. Web titrate fio2 and flow rate as required; Web the air and oxygen blender can set an inspiratory fraction of oxygen (fio2) from 21% up to 100% in a flow up to 60 l/min. This has become an increasingly utilised modality for the management. Higher l/min of flow provides some peep to the. Fio2 titratable up to 100%. The patient wears soft, pliable, wide‐bore nasal prongs, which fit snugly into the nares and are held in. Web this article describes the mechanism of action in an easy to remember mnemonic (hiflow); Web − nasal cannula that conserves oxygen by allowing oxygen to accumulate in the reservoir while the patient exhales. However, there is no consensus on the initial flow settings and. Web the fio2 when using nasal cannula depends on the flow rate (see ‘flowmeters‘), prong diameter in relation to nostril diameter, the patient’s size and the. The gas is heated and humidified and. Although certain factors, such as how fast you breathe and the size of your breaths, slightly impact the fio2, there's a pretty. Web titrate fio2 and flow rate as required; This has become an increasingly utilised modality for the management. Web while commonly used in infants, the development of newer systems for adults that reliably deliver warmed and humidified oxygen at high flows through nasal. An air/oxygen blender, allowing from 0.21 to 1.0 f i o 2, generates up to 60 l/min flow. Heated and humidified, meets inspiratory demands, increases. Web this activity reviews the use of a high flow nasal cannula and the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating and monitoring patients receiving high flow oxygen. − results in providing a higher fio2 when the patient inhales. Web high flow nasal cannula (hfnc) oxygen enables delivery of high inspired gas flows of air/oxygen blend. Heated humidified gas flow preserves nasal mucosa and is more comfortable allowing high. Web the air and oxygen blender can set an inspiratory fraction of oxygen (fio2) from 21% up to 100% in a flow up to 60 l/min. Web while commonly used. Web high flow nasal cannula (hfnc) oxygen enables delivery of high inspired gas flows of air/oxygen blend. The patient wears soft, pliable, wide‐bore nasal prongs, which fit snugly into the nares and are held in. Web this article describes the mechanism of action in an easy to remember mnemonic (hiflow); Higher l/min of flow provides some peep to the. Web. It delivers warm oxygen because oxygen at this flow rate. ‐wall oxygen source runs through a heater and humidifier. Web high flow nasal cannula (hfnc) oxygen enables delivery of high inspired gas flows of air/oxygen blend. Higher l/min of flow provides some peep to the. The physiological mechanism of action. Web this activity reviews the use of a high flow nasal cannula and the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating and monitoring patients receiving high flow oxygen. The physiological mechanism of action. Web high flow nasal cannula therapy is a type of respiratory support that delivers heated and humidified gas with a controlled concentration of oxygen to your patients.. It delivers warm oxygen because oxygen at this flow rate. Web the fio2 when using nasal cannula depends on the flow rate (see ‘flowmeters‘), prong diameter in relation to nostril diameter, the patient’s size and the. Although certain factors, such as how fast you breathe and the size of your breaths, slightly impact the fio2, there's a pretty. The gas. Web high flow nasal cannula (hfnc) oxygen enables delivery of high inspired gas flows of air/oxygen blend. High flow nasal cannula (hfnc): Although certain factors, such as how fast you breathe and the size of your breaths, slightly impact the fio2, there's a pretty. Web the air and oxygen blender can set an inspiratory fraction of oxygen (fio2) from 21%. The patient wears soft, pliable, wide‐bore nasal prongs, which fit snugly into the nares and are held in. Web the air and oxygen blender can set an inspiratory fraction of oxygen (fio2) from 21% up to 100% in a flow up to 60 l/min. However, there is no consensus on the initial flow settings and. It can deliver up to. Web this activity reviews the use of a high flow nasal cannula and the role of the interprofessional team in evaluating and monitoring patients receiving high flow oxygen. Fio2 titratable up to 100%. Web while commonly used in infants, the development of newer systems for adults that reliably deliver warmed and humidified oxygen at high flows through nasal. Web nasal. The patient wears soft, pliable, wide‐bore nasal prongs, which fit snugly into the nares and are held in. It can deliver up to about 60 liters of oxygen per minute. Web titrate fio2 and flow rate as required; The physiological mechanism of action. Web − nasal cannula that conserves oxygen by allowing oxygen to accumulate in the reservoir while the. The gas is heated and humidified and. − results in providing a higher fio2 when the patient inhales. The nc tubing is placed around a patient’s face with the prongs positioned at the nostrils. However, there is no consensus on the initial flow settings and. Web − nasal cannula that conserves oxygen by allowing oxygen to accumulate in the reservoir. Web high flow nasal cannula therapy is a type of respiratory support that delivers heated and humidified gas with a controlled concentration of oxygen to your patients. Heated humidified gas flow preserves nasal mucosa and is more comfortable allowing high. Higher l/min of flow provides some peep to the. Web titrate fio2 and flow rate as required; Web the fio2 when using nasal cannula depends on the flow rate (see ‘flowmeters‘), prong diameter in relation to nostril diameter, the patient’s size and the. Web high flow nasal cannula (hfnc) oxygen enables delivery of high inspired gas flows of air/oxygen blend. High flow nasal cannula (hfnc): The physiological mechanism of action. Web this article describes the mechanism of action in an easy to remember mnemonic (hiflow); This has become an increasingly utilised modality for the management. Web the use of heated and humidified high flow nasal cannula (hfnc) has become increasingly popular in the treatment of patients with acute respiratory failure. Web − nasal cannula that conserves oxygen by allowing oxygen to accumulate in the reservoir while the patient exhales. − results in providing a higher fio2 when the patient inhales. However, there is no consensus on the initial flow settings and. The nc tubing is placed around a patient’s face with the prongs positioned at the nostrils. The patient wears soft, pliable, wide‐bore nasal prongs, which fit snugly into the nares and are held in.Nasal Cannula O2 Rate The Relationship Between Oxygen Flow Rate And
High Flow Nasal Cannula FiO2 Chart
High Flow Nasal Cannula Fio2 Chart
Nasal Cannula Fio2 Calculation Table
High Flow Nasal Cannula Fio2 Chart
High Flow Nasal Cannula Flow Rate And Fio2 Oxymizer® Disposable
High Flow Nasal Cannula Fio2 Chart
High Flow Nasal Cannula Fio2 Chart
High Flow Nasal Cannula Fio2 Chart
High Flow Nasal Cannula FiO2 Chart
Web This Activity Reviews The Use Of A High Flow Nasal Cannula And The Role Of The Interprofessional Team In Evaluating And Monitoring Patients Receiving High Flow Oxygen.
Web Nasal Cannula Flow Rate And Fio2.
Web While Commonly Used In Infants, The Development Of Newer Systems For Adults That Reliably Deliver Warmed And Humidified Oxygen At High Flows Through Nasal.
Web The Air And Oxygen Blender Can Set An Inspiratory Fraction Of Oxygen (Fio2) From 21% Up To 100% In A Flow Up To 60 L/Min.
Related Post: