Peds Burn Chart
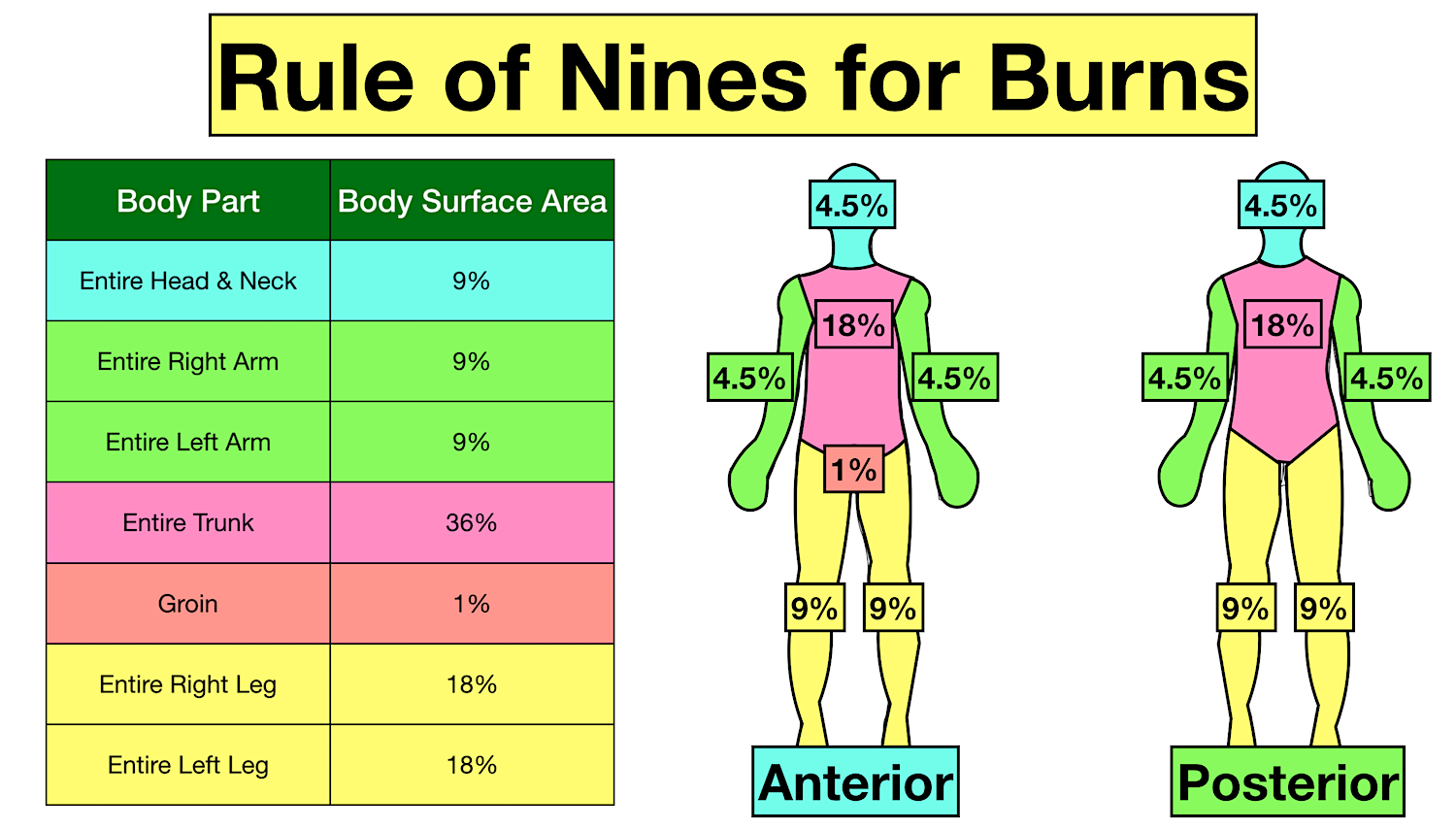
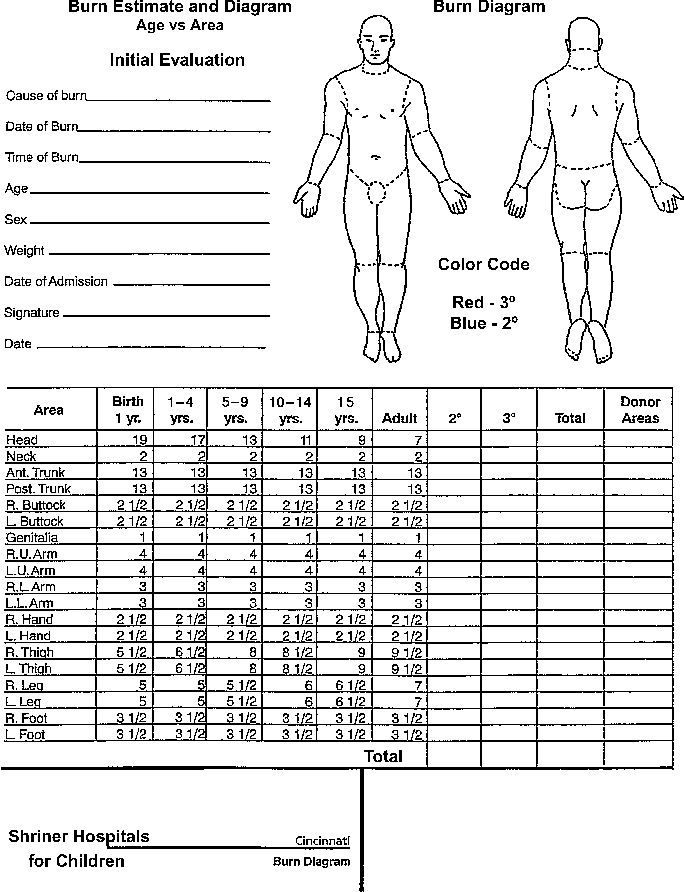
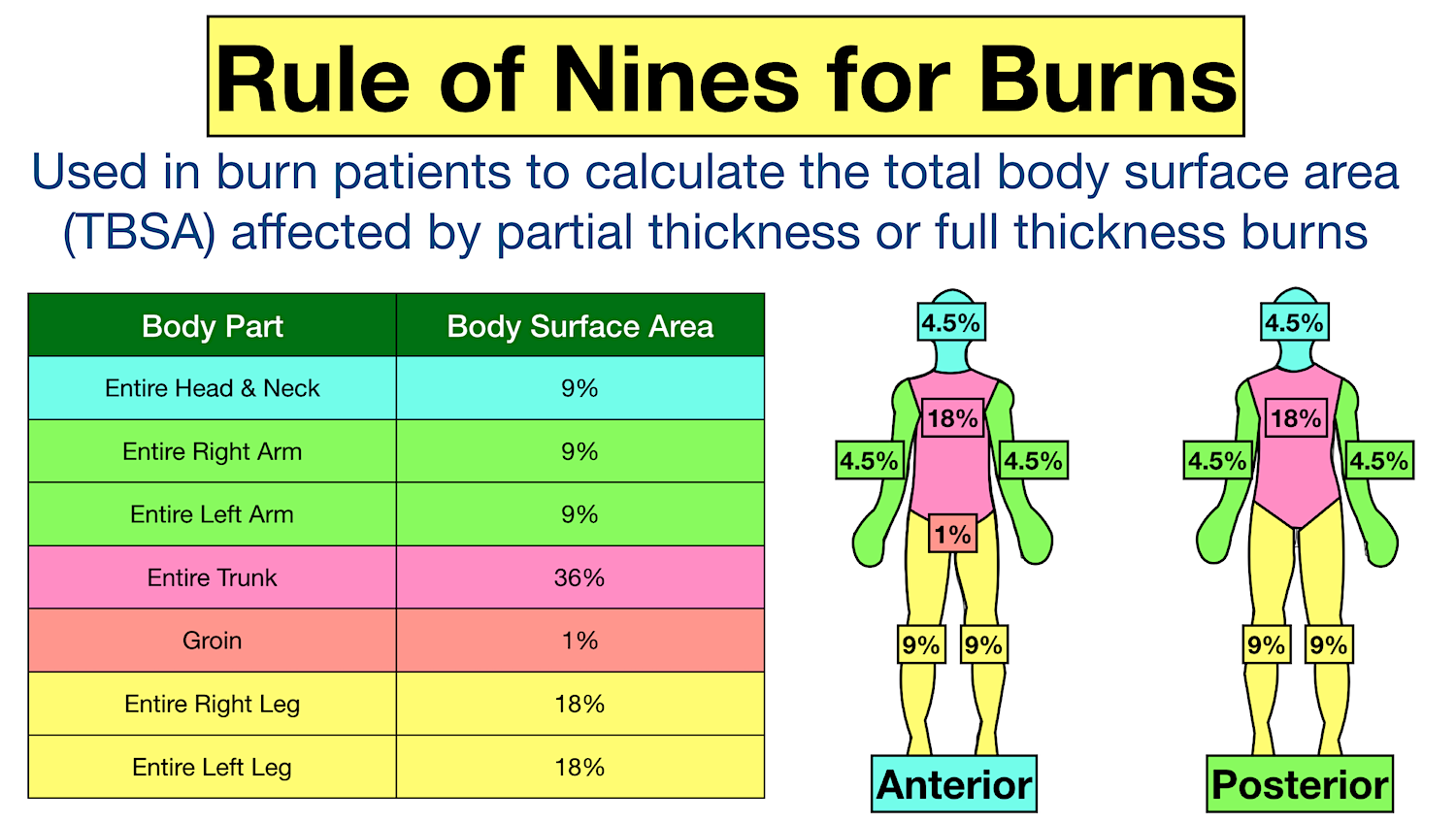
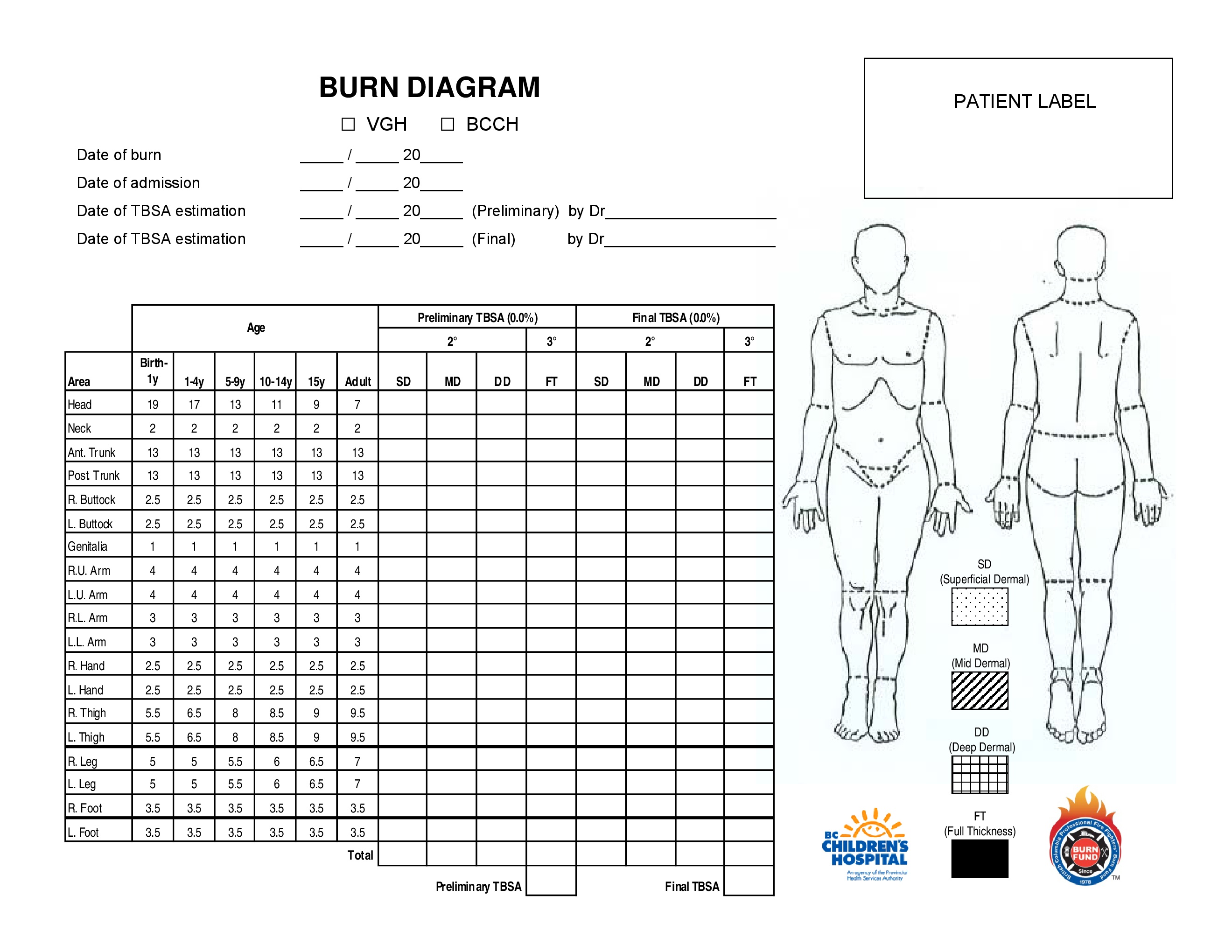
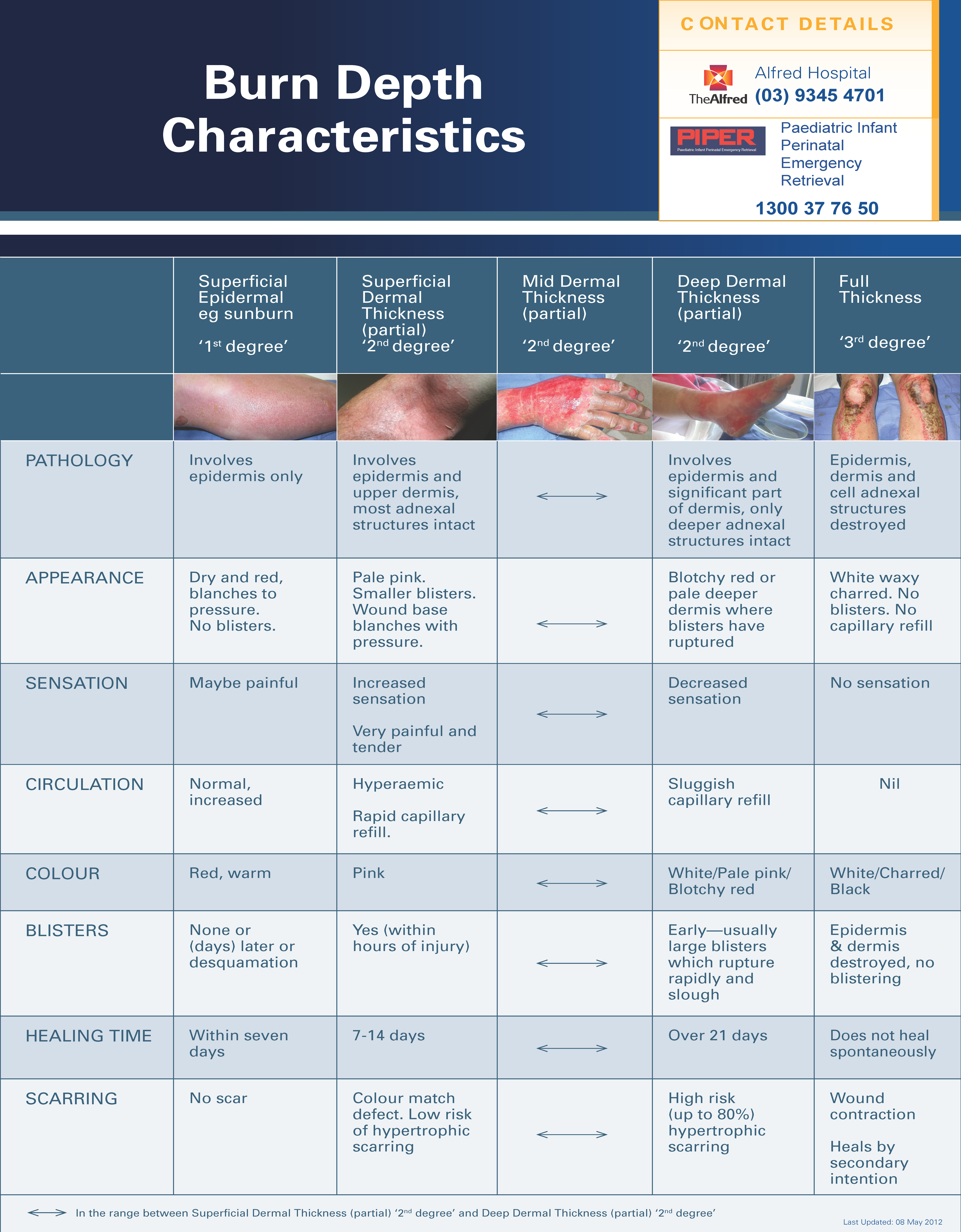
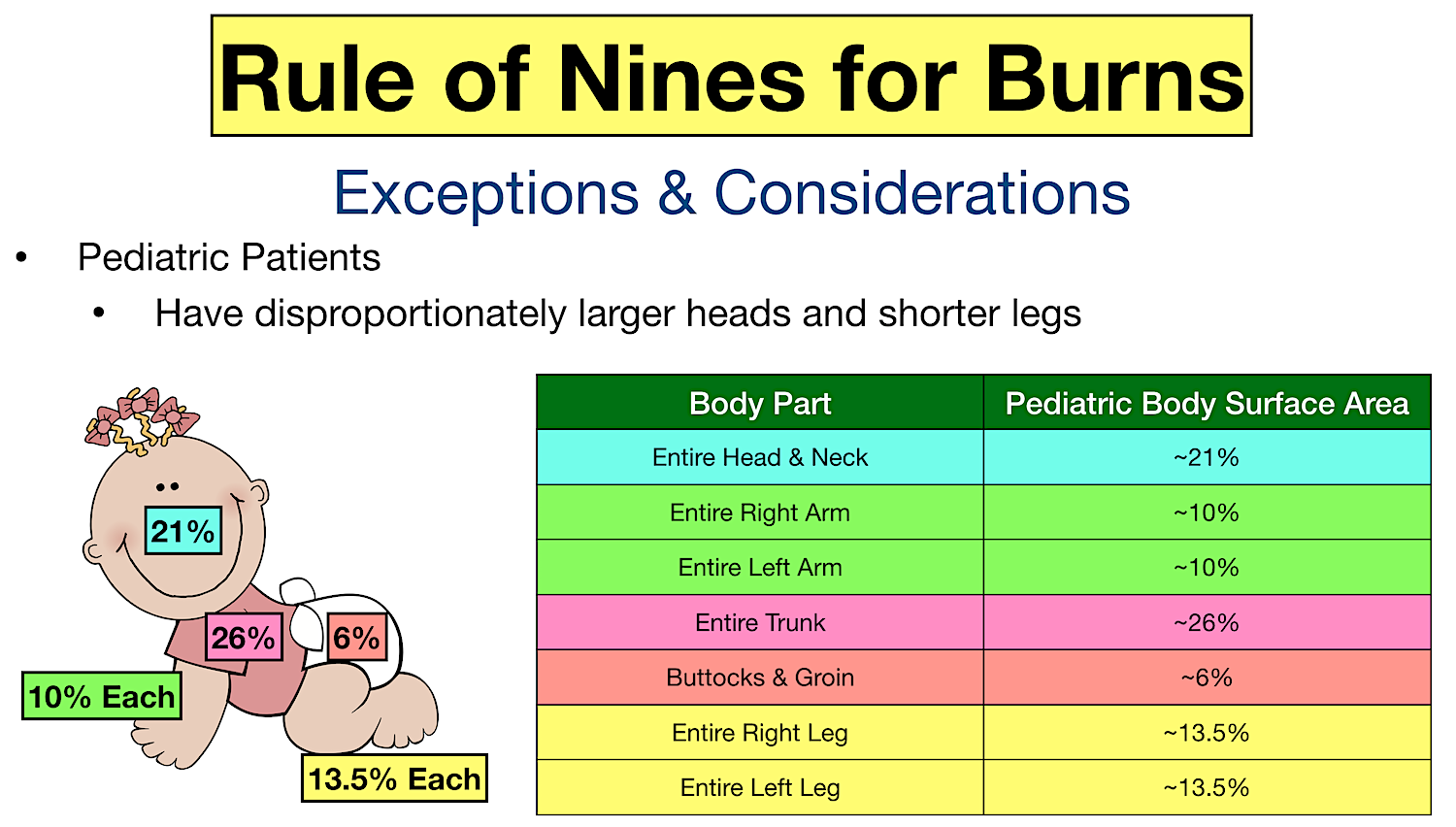
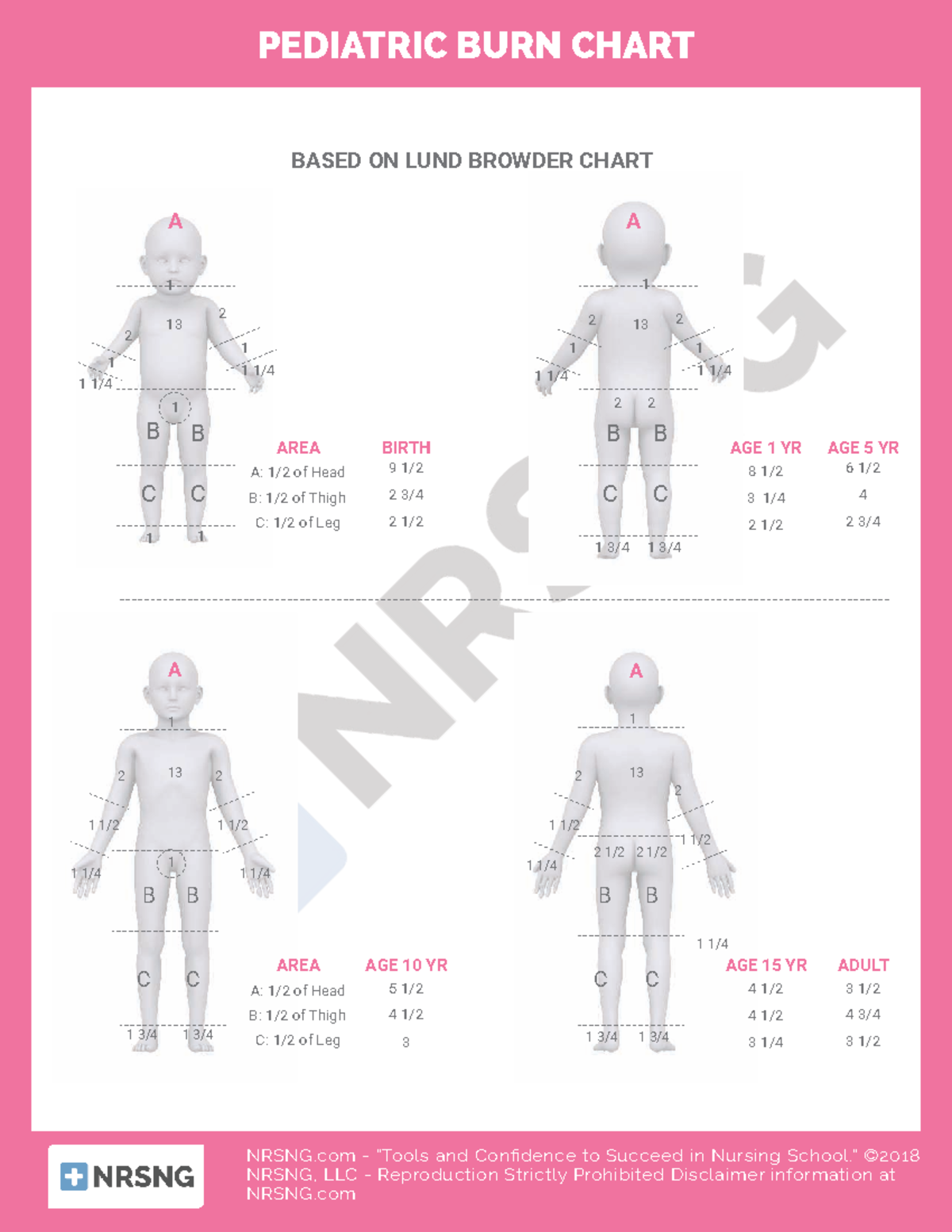
Peds Burn Chart - Nearly 75% of all scalding burns in children are preventable. Web pediatric burns are injuries to the skin or other tissue as a result of exposure to heat (eg, hot liquids [scalds], hot solids [contact burns], smoke [inhalation injury], or direct flames), ultraviolet/infrared radiation, radioactive materials, electricity, friction, chemicals, or cold. Includes charts, calculations, definitions, formulas, and example practice questions! Great for emts, pediatrics, nursing, and more! Management of these injuries and their consequences will be part of most busy general pediatric practices. To better delineate discharge criteria for admitted burn patients. Adults < 15%, peds < 10%; Children die from fire and burn injuries. Smoking and open flame are the leading causes of burn injury in adults. R in children under 4. Both infants and older adults are at the greatest risk for burn injury. Adult & baby calculation [emt, nursing] the rule of nines (9s) for burns in a child, infant, and adult. R in children under 4. Children are hospitalized with burn injuries. Burns are painful wounds caused by thermal, cold, electrical, chemical or electromagnetic energy. Web burn injuries are common in children. Rule of nines for burns made easy: The care of minor thermal burns, smoke inhalation, chemical burns to the skin and eye, electrical injuries, and ongoing burn management, are discussed separately. Calculate requirements from time of. Identify surface area of burn and significance guidelines and transport guidelines fluid management. Great for emts, pediatrics, nursing, and more! There are several methods to calculate tbsa. Web the paediatric burns centre (pbc) provides the only specialist dedicated paediatric burns centre in queensland according to the australian and new zealand burns association (anzba) guidelines. ( american burn association 2013 report) Both infants and older adults are at the greatest risk for burn injury. (see treatment of minor thermal burns.) *infants and the elderly have thinner skin; The care of minor thermal burns, smoke inhalation, chemical burns to the skin and eye, electrical injuries, and ongoing burn management, are discussed separately. Web to appropriately triage, diagnose and classify burns in the pediatric patient. Web pediatric burns are injuries to the skin or other tissue. Toddlers and children are more often burned by a scalding or flames. Web burns and fires are the fifth most common cause of accidental death in children and adults, and account for an estimated 3,500 adult and child deaths per year. Calculate requirements from time of. Dušica simić* ivana budić, ana vlajković, miodrag milenovic and marija stević *correspondence email: To. Adults < 15%, peds < 10%; Adult & baby calculation [emt, nursing] the rule of nines (9s) for burns in a child, infant, and adult. (see treatment of minor thermal burns.) ( american burn association 2013 report) Web use the “rule of nines” to estimate burn size for adult and pediatric. (see treatment of minor thermal burns.) The extent of large tbsa burns is often underestimated, and factors such as sex, body shape,. ( cdc.gov) 2 children die every day due to burn related injuries. Adults > 20%, peds > 15%; *infants and the elderly have thinner skin; Great for emts, pediatrics, nursing, and more! Child & adult chart calculations. ( american burn association 2013 report) Web the goal is management of burns shock, through optimal replacement of fluid losses to maximise wound and body perfusion, and minimise wound and body oedema and associated adverse effects. There are several methods to calculate tbsa. Nearly 75% of all scalding burns in children are preventable. Rule of nines for burns made easy: Web pediatric burns are injuries to the skin or other tissue as a result of exposure to heat (eg, hot liquids [scalds], hot solids [contact burns], smoke [inhalation injury], or direct flames), ultraviolet/infrared radiation, radioactive materials, electricity, friction, chemicals, or cold. There are. Child & adult chart calculations. Children are hospitalized with burn injuries. Include only partial (second degree) and full thickness (third degree) burns. R in children under 4. Many burn centers prefer lactated ringers unless shock liver or hepatic failure suspected; There are several methods to calculate tbsa. Adults > 20%, peds > 15%; *infants and the elderly have thinner skin; An alternative rule is that the patient's palm and fingers represent 1% of the body surface. Dušica simić* ivana budić, ana vlajković, miodrag milenovic and marija stević *correspondence email: Smoking and open flame are the leading causes of burn injury in adults. Include only partial (second degree) and full thickness (third degree) burns. Burns are painful wounds caused by thermal, cold, electrical, chemical or electromagnetic energy. Web rule of nines for burns: Web infant/pediatric lund and browder burn chart. 80% to 90% of all severe burns occur in low to middle income countries. Toddlers and children are more often burned by a scalding or flames. Children die from fire and burn injuries. Include only partial (second degree) and full thickness (third degree) burns. >500,000 people affected by burn injuries each year. To better delineate discharge criteria for admitted burn patients. Adult & baby calculation [emt, nursing] the rule of nines (9s) for burns in a child, infant, and adult. Adults > 20%, peds > 15%; Identify surface area of burn and significance guidelines and transport guidelines fluid management. Angela gibson, md, phd melissa beltran, msn, rn, ccrn. Although most burns in children are small and can be managed with care provided in the outpatient setting, there is a significant number of children with more serious. Consequently, burns may be deeper and more severe than they initially appear (american burn association, 2018). Management of these injuries and their consequences will be part of most busy general pediatric practices. There are several methods to calculate tbsa. Web indications based on total body surface area of burn. Categorize burn depth and its significance.Rule of Nines for Burns Child and Adult Chart, Calculator, Definition
Pediatric Burn Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Parkland Formula for Burns Pediatric and Adult Examples, Calculator
PEDIATRIC BURNS AND SCALDSMODERN THERAPEUTIC CONCEPTS Semantic Scholar
Rule Of Nines Pediatric Burn Chart
Pediatric Burn Diagram
Paediatric TraumaPaediatric Burns Sub Guideline Trauma Victoria
Rule of Nines for Burns Child and Adult Chart, Calculator, Definition
Major Burns in Children Pediatric Emergency Playbook
Cspeds001pediatric burn chart NRSNG “Tools and Confidence to
Web Pediatric Burn Care.
(See Treatment Of Minor Thermal Burns.)
The Extent Of Large Tbsa Burns Is Often Underestimated, And Factors Such As Sex, Body Shape,.
Web Burns And Fires Are The Fifth Most Common Cause Of Accidental Death In Children And Adults, And Account For An Estimated 3,500 Adult And Child Deaths Per Year.
Related Post: