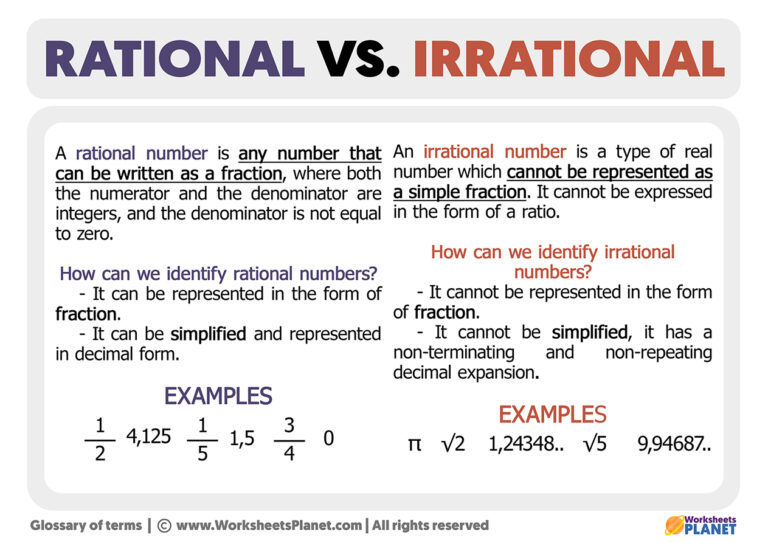
Rational Irrational Numbers Chart
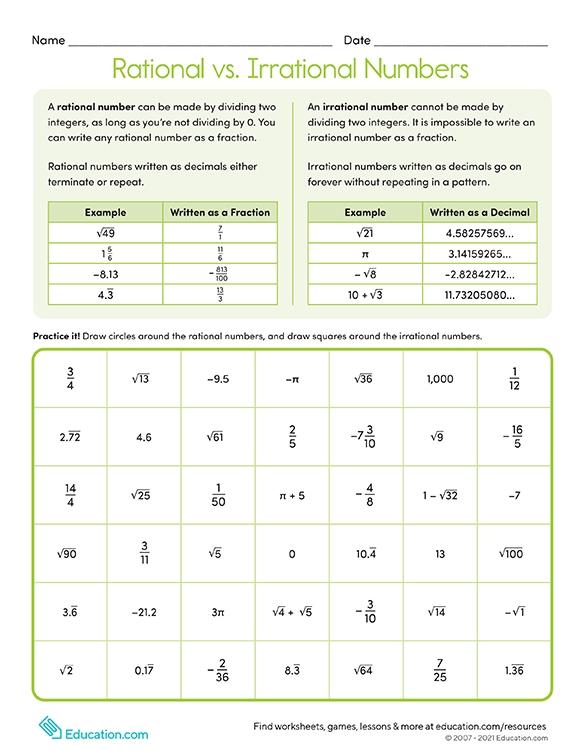
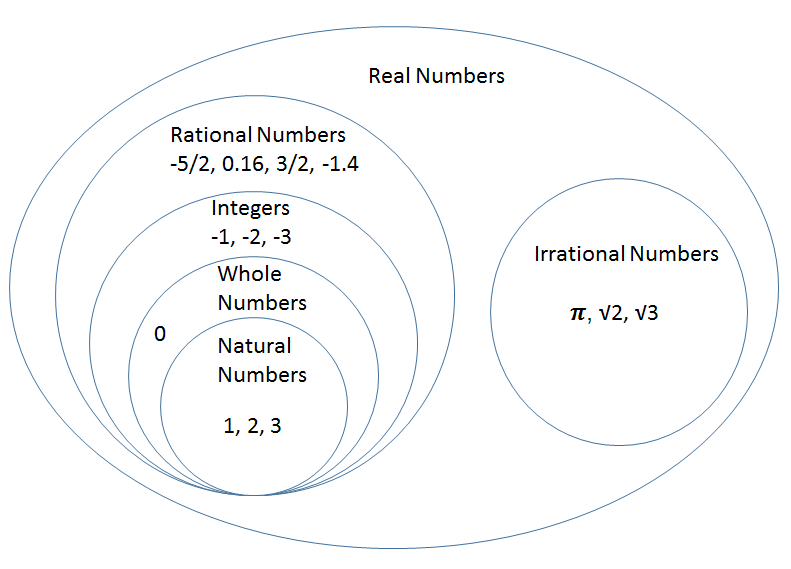
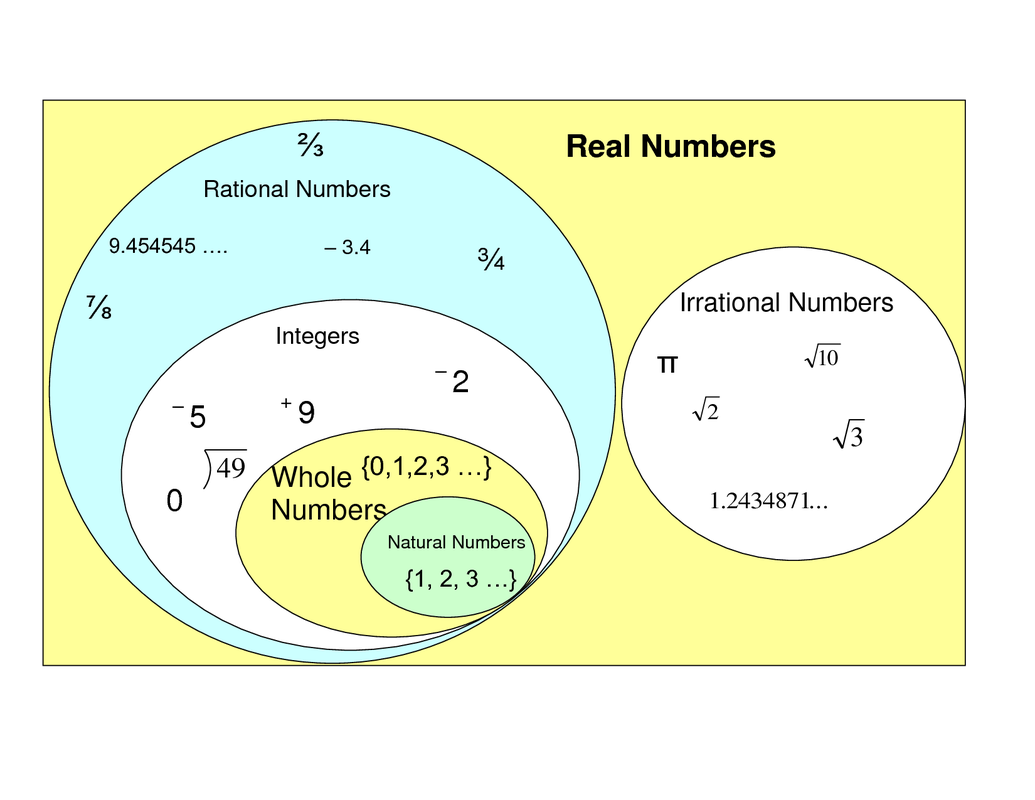
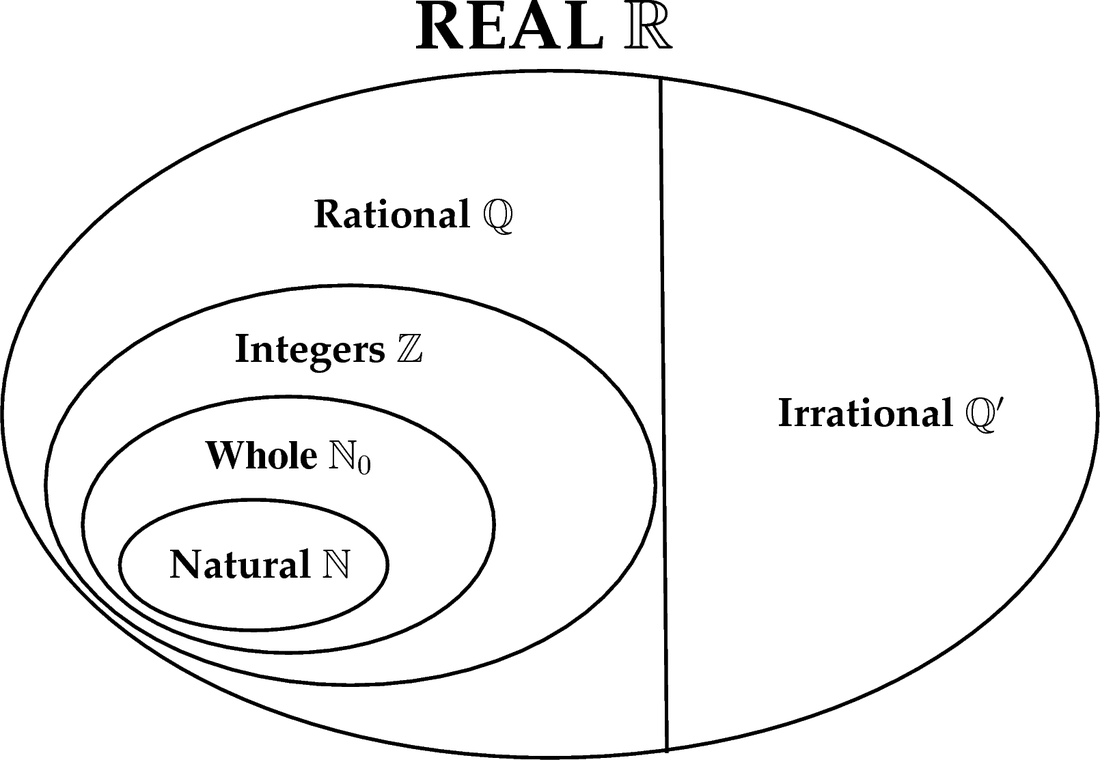
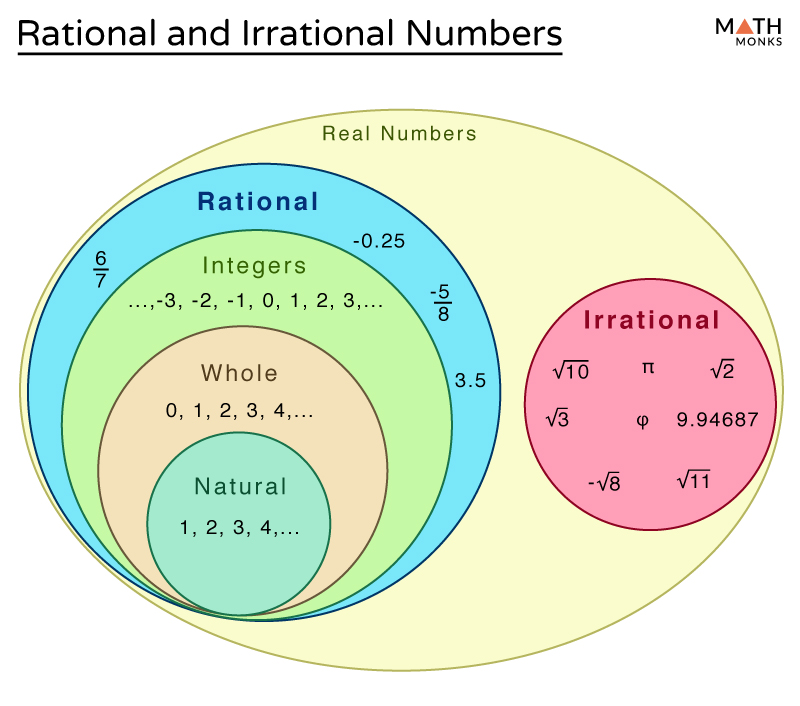
Rational Irrational Numbers Chart - A irrational number is a number which cannot be expressed in a ratio of two integers. For example, √3 × √3 = 3; The most common rational numbers are positive and negative integers. Web differences between rational and irrational numbers. Identifying rational and irrational numbers math www.commoncoresheets.com name: ⅔ is an example of a rational number whereas √2 is an irrational number. All real numbers that are not rational numbers; Numbers such as pi are irrational numbers, as there is no ratio of integers that can. The rational numbers include all the integers because any integer z can be expressed as the ratio z 1. Web comparing irrational numbers with a calculator get 5 of 7 questions to level up! Web in your own words, explain the difference between a rational number and an irrational number. Its decimal form does not stop and does not repeat. Rational numbers can be expressed as a ratio between two integers. A rational number can be written as a ratio of two integers (ie a simple fraction). To identify rational and irrational numbers, we have to know about their definitions and differences first. Comparing irrational numbers with a calculator. Web the venn diagram below shows examples of all the different types of rational, irrational numbers including integers, whole numbers, repeating decimals and more. This is the basic definition of a rational number. All the numbers that can be found on a number line. What are rational and irrational numbers. This is the basic definition of a rational number. Its decimal form does not stop and does not repeat. Identifying rational and irrational numbers math www.commoncoresheets.com name: Web differences between rational and irrational numbers. By contrast, irrational numbers are any numbers that cannot take the form of a ratio of integers. All the numbers that are not rational are called irrational. But an irrational number cannot be written in the form of simple fractions. The most common rational numbers are positive and negative integers. Comparing irrational numbers with a calculator. 7 is rational, because it can be written as the ratio 7/1. For example, √3 × √3 = 3; 𝜋=3.14159…, √3=1.73205, euler’s constant, etc. Web differences between rational and irrational numbers. The rational numbers include all the integers because any integer z can be expressed as the ratio z 1. Rational numbers can be written as fractions and ratios. Web determine if the number is rational (r) or irrational (i). Stops or repeats, the number is rational. All the numbers that can be found on a number line. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. To identify rational and irrational numbers, we have to know about their definitions and. When any irrational numbers multiplied by any nonzero rational number, their product is an irrational number. Web the venn diagram below shows examples of all the different types of rational, irrational numbers including integers, whole numbers, repeating decimals and more. The letter ‘ p denotes an irrational number.’. The rational numbers include all the integers because any integer z can. A irrational number is a number which cannot be expressed in a ratio of two integers. Web rational numbers are those that can be expressed in the form of p/q, where q does not equal to 0, and irrational numbers are those that cannot. Web in your own words, explain the difference between a rational number and an irrational number.. Irrational numbers, when written as a decimal,. A rational number can be written as a ratio of two integers (ie a simple fraction). Rational numbers, irrational numbers, and roots: If the decimal form of a number. Set of real numbers venn diagram examples of rational numbers Web for an irrational number x, and a rational number y, their result, x+y = an irrational number. Web determine if the number is rational (r) or irrational (i). All real numbers that are not rational numbers; The rational numbers include all the integers because any integer z can be expressed as the ratio z 1. Web comparing irrational numbers. Web learn the difference between rational and irrational numbers, learn how to identify them, and discover why some of the most famous numbers in mathematics, like pi and e, are actually irrational. A few examples of irrational numbers are π , 2 ,. A rational number can be written as a ratio of two integers (ie a simple fraction). Numbers. Numbers such as pi are irrational numbers, as there is no ratio of integers that can. The letter ‘ p denotes an irrational number.’. Introduction to rational and irrational numbers. Web learn the difference between rational and irrational numbers, learn how to identify them, and discover why some of the most famous numbers in mathematics, like pi and e, are. This is the basic definition of a rational number. Closure property, commutative property, associative property, identity property and distributive property. For an irrational number x and a rational number y, their product xy = irrational. When any irrational numbers multiplied by any nonzero rational number, their product is an irrational number. 7 is rational, because it can be written as the ratio 7/1. Web the product of two irrational numbers may or may not be rational. The number ½ is a rational number because it is read as integer 1 divided by integer 2. A irrational number is a number which cannot be expressed in a ratio of two integers. 𝜋=3.14159…, √3=1.73205, euler’s constant, etc. The rational numbers include all the integers because any integer z can be expressed as the ratio z 1. ⅔ is an example of a rational number whereas √2 is an irrational number. All the numbers that can be found on a number line. The technical definition of an irrational number is that it is a “real number which is not a rational number.” so what does an irrational number look like? Check the chart below, to differentiate between rational and irrational. A rational number can be written as a ratio of two integers (ie a simple fraction). Web comparing irrational numbers with a calculator get 5 of 7 questions to level up!What's the Difference Between Rational and Irrational Numbers? in 2021
Rational Versus Irrational Numbers Worksheet
Rational And Irrational Chart
Rational Numbers Lefere Math
Rational Numbers Anchor Chart
Rational Irrational Numbers Chart
Rational Numbers Lefere Math
Rational And Irrational Numbers
Rational vs. Irrational Numbers 4 Key Differences, Definition
Rational And Irrational Numbers Chart
If The Decimal Form Of A Number.
The Definitions Followed By Examples Are As Follows:
Its Decimal Form Does Not Stop And Does Not Repeat.
Introduction To Rational And Irrational Numbers.
Related Post: